Honors -Final Exam Flashcards
(352 cards)
How to calculate neutrons:
of Neutrons = Atomic Mass Number - Atomic Number
Electron Configuration
A shorthand method of writing the location of electrons by sublevels.

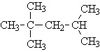
How do the bulk properties of polymers effect their behavior?
Linear structure - thermoplastics (can be melted and thus recycled.)
Branched chains - strengthen the structure of thermoplastics
Loosely Cross Linked Chains - loosely cross linked structures form an elastomers (rubber)
Tightly Cross Linked Chains - thermoset plastics (can not be melted and thus can not be recycled)
A polymer’s architecture affects many of its physical properties including, but not limited to, solution viscosity, melt viscosity, solubility in various solvents, glass transition temperature and the size of individual polymer coils in solution.
Combustion
Any compound formed from only Carbon an Hydrogen (fuel) added to Oxygen to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
What happens to an exothermic reaction when temperature is increased?
Heat is a product, so the reaction shifts to the left to make more reactant.
How to determine if a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated.
Add more solute and observe the results.

Acids
Electron acceptors.
Yeild H+ Ions in solution.
H+ donor.

Write the formula for Mg²⁺ and PO₄³⁻
Using the criss-cross method and subscripts to insure sum of charges is zero: Mg₃(PO₄)₂
Ionic Compounds
Conduct Electricity when melted or dissolved in water because….

What happens to an endothermic reaction when temperature is increased?
Heat is a reactant, so the reaction will shift to the right to make more product.
The Mole
A unit of measure.
1 mole = the atomic mass of an element
and
1 mole = 6.02 E23 atoms, particles, molecules, units, etc.
Solid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter. It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume.
Orbital
Sublevels can be broken down into regions called “orbitals”. An orbital is defined as the most probable location for finding an electron. Each orbital holds 2 electrons.

Thermochemistry
The study of energy changes during a chemical reaction or change of state (solid, liquid, gas).
Ionic Compounds
two words, first names cation second names anion. Indicate charge of transition metal cation by Roman Numeral. MgCl₂ = Magnesium Chloride Cr(NO₃)₃ = Chromium(III) Nitrate SnCl₂ = Tin(II) Chloride
Calculate the % Yield of solid silver chromate produced in the following reaction:
K₂CrO₄ + 2AgNO₃ → Ag₂CrO₄ + 2KNO₃
In the reaction there was .500g of the limiting reactant AgNO₃. In the actual experiment, .455g of Ag₂CrO₄ was produced.
Calculating the Theoretical Yield of Ag₂CrO₄ that was produced:
0.500g AgNO₃ x (1 mole AgNO₃ / 169.9g AgNO₃) x
(1mole Ag₂CrO₄ / 2 mole AgNO₃) x (331.7 g Ag₂CrO₄ / 1 mol Ag₂CrO₄) =0 .488g Ag₂CrO₄.
Find the ratio of the actual yield (.455g) to the theoretical yield (.488g) …
% Yield = (.455g Ag₂CrO₄ ÷ .488g Ag₂CrO₄ ) x 100 =
93.2 %
Amphoteric

Acid or Base
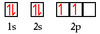
What is the electron configuration of Vanadium?
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d³
[Ar] 4s² 3d³
Intramolecular Forces
Attractive forces WITHIN a molecule (Ionic & Covalent Bonds)
These bonds are stronger than intermolecular forces.
Single Replacement
An element and a compound are located on each side of the equation. The Activity Series must be checked to determine if the reaction will occur. If the reaction occurs, the element on the reactant side switches with the similarly charged ion within the compound on the reactant side.
A + BC –> AC + B

Melting
Make or become liquefied by heat. (Solid to Liquid)
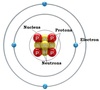
Atomic Number
Identifies an element. The number of protons. For a neutral atom, the number of electrons will equal the number of protons. For an ion (charged atom) the number of electrons will not be the same as the atomic number.

Reactants

Substances being mixed in a chemical reaction. The left side of the equation.
Predict the products of and write a balanced equation from the following statement:
H₂O₂ →
H₂O₂ → H₂ + O₂
DECOMPOSITION