Human development Flashcards
(34 cards)
What happens during an orgasm?
What happens during an orgasm?
Two ways the journey of the sperm assisted?
Mechanical ways the sperm is assisted
> uterus and uterine tube contracts occurring in orgasmic phase (female) >Flagellum (male) >Uterine and uterine tube cillia(female)
Chemical ways the sperm is assisted
>Oxytocin from posterior pituitary (female) >Prostaglandins from semen
How long does the spermatozoa arrive in the uterine tube?
2-7 hours post coitus
Two ways the journey of the sperm assisted?
Mechanical ways the sperm is assisted
> uterus and uterine tube contracts occurring in orgasmic phase (female) >Flagellum (male)
>Uterine and uterine tube cillia(female)
Chemical ways the sperm is assisted
>Oxytocin from posterior pituitary (female) >Prostaglandins from semen
How long does the spermatozoa arrive in the uterine tube?
2-7 hours post coitus
What is fertilisation?
- fertilisation involves the fusion of two haploid gametes
How many chromosomes are in each hapoid gamete?
23 chromosomes
Where does fertilisation ussueally occur?
- near the junction between the ampulla and isthmus of the uterine tube
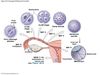
Step 1 of fertilisation
- Ovulation releases a seconary oocyte and the first polar body
- Both are surrounded by the corona radiata
- The oocyte is suspended in metaphase of meiosis II
Step 2 of fertilisation
Fertilisation and oocyte activation
- Acrosomal enzymes from multiple spermatozoa create gaps between the cells of corona radiata
- A single sperm then makes contact with the oocyte membrane and membrane fussion occurs, triggering oocyte activation
- The secondary oocyte is now an ovum
Step 3 of fertilisation
Pronucleus formation begins
- The sperm is absorbed into the cytoplasmm and the female nuclear material within the ovum reorganises as the female pronucleus
Step 4 of fertilisation
Spindle formation and cleavage preparation
- The male pronucleus develops, and spindle fibers appear in preparation for cell division
- This is the strat of the process of cleavage, a series of cell divisions that produces an increasing number of smaller and smaller daughter cells.
Step 5 of fertilisation
Amphimixis occurs and cleavage begins
- The pronucleus migrates toward the center of the ovum, where the spindle fibers are forming
- The two pronuclei then fuse in a process called amphimixis
- The cell is now a zygote containinfg 46 chromosomes
- Fertilisation is now complete
Step 6 of fertilisation
Cytokinesis begins
- The first cleavage division nears completion about 30 hours after fertilisation
- This produces two daughter cells, each one-half the size of the original zygote.
- These cells are called blastomeres.
Explain oocyte activation
- is a series of changes in the metabolic activity of the oocyte leading to Ca+ release from the smooth ER.
- The rise in Ca+ has three effects
- Enzymes are released that prevent fertilisation by more than one sperm
- completion of meiosis II and formation of the second polar body
- Activation of enzymes that cause a rapid increase in the cells metabolic rate
What happens during cleavage?
The cytoplasm of the zygote becomes subdivided among an increasing number of progressively smaller blastomeres,
How long does cleavage last?
About 7 days
Day 0
Fertilisation