Hydrocarbons (T5) Flashcards
(8 cards)
What are hydrocarbons?
Compounds containing hydrogen and carbon only. Hydrocarbons are organic molecules.

How do the properties of hydrocarbons change as the molecules get bigger?
The boiling point increases: - large molecules are attracted to each other more strongly than smaller ones - more heat is needed to break these stronger attractions to produce the widely separated molecules in the gas The liquids become less volatile: - the bigger the hydrocarbon the more slowly it evaporates at room temperature - this is also because the bigger molecules are more strongly attracted to their neighbours and do not turn into a gas so easily The liquids flow less easily (become more viscous): - liquids containing small hydrocarbon molecules are runny - those containing large molecules are much stickier because of the greater attractions between their molecules Bigger hydrocarbons do not burn as easily: - this limits the use of bigger ones as fuels
All hydrocarbons burn in air (oxygen) to form…
Carbon dioxide + water (and a lot of heat in the process)
What is cracking?
A useful process which breaks large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones. Eg: the big hydrocarbon molecules in gas oil can be broken down into the smaller ones needed for petrol.
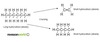
What are the two main problems with normal crude oil distillation and how can cracking help?
The amount of each fraction you get in crude oil distillation will depend on the proportions of the various hydrocarbons in the original crude oil. Eg: far more petrol is needed than is found in crude oil. Also apart from burning, the hydrocarbons in crude oil are fairly un-reactive. To make other organic chemicals from them they must first be converted into something more reactive. Cracking can break down the big hydrocarbon molecules in gas oil into the smaller ones needed for petrol. The majority of hydrocarbons found in crude oil have single bonds between the carbon atoms. During the cracking process, molecules are also formed that have double bonds between the carbon atoms. These new molecules are much more reactive and can be used to make many other things.
How does cracking work?
The gas oil fraction is heated to give a gas and passed over a catalyst of mixed silicon dioxide and aluminium oxide at about 600-700 deg. C. This can also be carried out at higher temperatures without a catalyst.
In what form can hydrocarbons exist?
- chains - branched chains - rings - a combination


