images Flashcards
(58 cards)
- Modality
radiologic sign
diagnosis

-
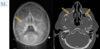
Modality:
- FLAIR (left) and DWI (right) MRI (noncontrast sequences)
- Region: brain, axial view
- Radiologic sign: hypertintense lesion representing edema and restricted diffusion in the territory of the right basal ganglions
- Diagnosis: small acute infarction
2.

-
Modality:
- DWI MRI (left) and
- 3D TOF (time-of-flight) angiography (noncontrast sequences)
- Region: brain, axial view
-
Radiologic sign:
- significant hyperintensity (representing restricted diffusion) in the right parietal lobe with concomitant abrupt filling defect at the right middle cerebral artery
-
Diagnosis:
- large acute infarction, acute thrombosis of the right middle cerebral artery
- Modality
region
radiologic sign
diagnosis

-
Modality: Non-enhanced CT, brain window setting
- (window level: 40 HU; window width: 80 HU)
- Region: Brain, axial view
-
Radiologic sign:
- (blue area) : Cortical-subcortical border disappeared/blurred due to edema
- (yellow arrow) : “hyperdense media”-sign – acute thrombosis of the right middle cerebral artery
-
Diagnosis:
- Subacute ischaemia in the territory of the right MCA
4.

-
Modality:
- Non-enhanced CT,
- brain window setting (window level: 40 HU; window width: 80 HU)
- Region: Brain, axial view
-
Radiologic sign:
- Extensive hypodense (20-25 HU) brain parenchyma,
- concomitant dilatation of the right lateral ventricle (arrows) due to brain tissue loss;
- green arrow : calcifications of the choroideal plexuses (common finding)
-
Diagnosis:
- Chronic ischemic lesion in the territory of right MCA
4.
5.

-
Modality:
- Non-enhanced CT,
- brain window setting (window level: 40 HU; window width: 80 HU)
- Region: Brain, axial view
-
Radiologic sign:
- Large hyperdense area (density: 60-70 HU) extending into the ventricles, slight midline shift to the right and compressed right lateral ventricle due to mass effect (yellow arrow)
-
Diagnosis:
- Acute cerebral apoplexy, most commonly caused by hypertensive crisis
apoplexy : unconsciousness or incapacity resulting from a cerebral haemorrhage or stroke.
6.

-
Modality:
- T2W MRI and 3D TOF angiography (noncontrast)
- Region: brain, axial view
-
Radiologic sign:
- enlarged “flow-void” on T2W MRI,
- circumscribeddilatation of the right internal carotid artery on TOF
- Diagnosis: aneurysm of theright internal carotid artery (cavernous part)
7.

- Modality: Non-enhanced CT
- Region: Brain, axial view
-
Radiologic sign:
- Cast-like hyperdensity filling the basal cisterns and sulci (normal hypodens, liquor-filled cysterns can be observed on the right image)
-
Diagnosis:
- Acute subarachnoid hemorrhage, most commonly due to a berry aneurysm rupture
8.

-
Modality:
- left –SWI axial MRI(magnitude image);
- middle –T2WI axial MRI;
- right –T1W sagittal MRI, noncontrast sequences
-
Region:
- Brain, axial and sagittal views
-
Radiologic sign:
- crescent-shaped hyperintense area on all sequences in the subdural space
-
Diagnosis:
- left-sided subdural hematoma, most commonly caused by the rupture of the bridge veins
9.

-
Modality:
- Non-enhanced CT ;
- left – brain window setting (window level: 40 HU; window width: 80 HU),
- right – bone window setting (window level: 600 HU; window width: 2800 HU)
-
Region:
- Brain, axial views
-
Radiologic sign:
- Lens-shaped hyperdense mass and skull vault fracture at the identical position (yellow arrow)
- Diagnosis: Right-sided epidural hematoma
10.

-
Modality:
- left panels –noncontrastCT,
- right panels –CE T1WI MRI (upper–sagittalview, lower–axialview) after iv. gadolinium administration
-
Region:
- Brain, axial and sagittalviews
-
Radiologic sign:
- Intraaxialparenchymal mass with rim-enhancement, which compresses the right lateral ventricle (arrow);
- MRI’s superior soft tissue resolution over CT’s is clearly oservable
- Diagnosis: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM)
10.
11.

-
Modality:
- left – DWI MRI;
- middle – CE T1W SE with fat saturation MRI after iv. gadolinium administration;
- right – T2W fatsat MRI (axial view)
- Region: Brain, axial views
-
Radiologic sign:
- bilateral enhancing intrabulbar masses,
- restricted diffusion
- Diagnosis: bilateral retinoblastoma
12.

-
Modality:
- Non-enhanced MRI
- (left: T1WI sagittal,
- center: T2WI sagittal,
- right: T2WI axial)
-
Region:
- Lumbar spine
-
Radiologic sign:
- Btw L2/3 hypointense(signing low water content) discprotrudesinto the spinal canal (yellow arrow)
-
Diagnosis:
- Discherniation between L2 and L3 level; dehydrated disc(s)
13

-
Modality:
- left – T1W fatsat postcontrast MRI after iv. gadolinium administration;
- right – T2W fatsat MRI (sagittal view)
- Region: thoracic spine
-
Radiologic sign:
- epidural enhancing mass at the level of Th 9-12th vertebras,
- no signal loss on fatsat image;
- non-enhancing fluid signal intensity inside of the mass
- Diagnosis: epidural abscess
14

14.
Modality:
Noncontrast CT
Region:
Upper abdomen, axial views
Radiologic sign:
-Diffusely & homogenously decreased density (cca. -20 HU) of the liver
(normal density is cca. 50-60 HU).
-The vessels (blue arrows) → denser -relative to the liver parenchyma-
Diagnosis:
Steatosis Hepatis (Fatty liver)
15

-
Modality:
- Contrast-enhanced CT,
- portal phase,
- iv. iodine-based contrast agent
- Region: Upper abdomen, axial view
-
Radiologic sign:
- Multiple hypoenhancing lesions of the liver, normal spleen
- Diagnosis: Multiple liver metastases (most commonly from colon adenocc.)
-
Modality :
- Liver ultrasound with convex probe (3.5-5 MHz),
- B-mode
- Region: Liver, right subcostal view
- Radiologic sign: Hypoechoic lesions of the liver
- Diagnosis: Multiple liver metastases
16

Modality:
FDG PET-CT (right panel: non-contrast CT) → 18(F)-fluoro-deoxy-glucose
Region:
upper abdomen, axial view
- *Sign:**
- increased focal uptake in the liver
- physiological high up take in the kidney
Diagnosis:
Malignant tumor → colorectal cc. metastasis → liver
16.
17

-
Modality:
- PET-CT, 18-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) radiotracer;
- Hybrid imaging method: PET – metabolic activity,
- CT – morphology
-
Region:
- Whole-body, coronal view
-
Radiologic sign:
- Increased fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) uptake in liver and pubic bone,
- high physiologic activity is shown in the bladder (normal finding)
-
Diagnosis:
- Multiple metastases (liver, pubic bone)
18

- *Modality:**
- left –contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) after iv. microbubble administration (arterial phase)
- right–CEUS, late phase
Region:
liver right subcostal view
- *Radiologic sign:**
- Hepatic mass (peripheral nodular enhancement) -in the arterial phase- (L)
- complete filling in the late phase (R)
Diagnosis:
Hepatic hemangioma
19

-
Modality:
- Digital subtraction angiography (DSA), intraarterial iodine-based contrast agent; noncontrast CT (inlet)
- Region: Upper abdomen, liver
-
Radiologic sign:
- large hepatic mass in the righ lobe with intensive arterial supply, (hyperdense mass after embolization - inlet);
- selective catheterization of the right hepatic artery
-
Diagnosis:
- transcatheter arterial embolization of a giant hepatic hemangioma with Lipiodol; Lipiodol appears hyperdense on the noncontrast CT
21

-
Modality:
- left – Noncontrast CT,
- right – Contast-enhanced CT, iv. iodine-based contrast agent
- Region: Upper abdomen
-
Radiologic sign:
- Enlarged pancreas with indistinct margins;
- yellow arrow: Enhancing head – living tissue;
- red arrow : Non-enhancing body necrosis
- increased density of the surrounding mesenterial fat (fat necrosis);
- decreased liver density (see Image 14)
- Diagnosis: Acute necrotizing pancreatitis; fatty liver
20

Modality:“mDIXON” dynamic contrast-enhanced MR after iv. gadolinium
(noncontrast, arterial phase, portal phase, venous phase)
Region:
upper abdominal MR study (axial view)
- *Radiologic sign:**
- large hepatic mass
- intensive arterial enhancement
- no „wash-out”
- non-enhancing/hypointense central scar (red arrow)
Diagnosis:
hepatic focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)
22

- *Modality:**
- Ultrasound of gallbladder with convex probe (3.5–5 MHz)
- B-mode
- *Region:**
- Gallbladder
- right subcostal view
- *Radiologic sign:**
- Yellow arrow → Echo-dense structure in the gallbladder lumen, with acoustic shadowing
- Red arrow → Thick, stratified, oedematous wall
Diagnosis:
Acute cholecystitis with gallstone
23

-
Modality:
- T2W MRI, axial plane (left);
- 3D MRCP (heavily T2-weighted sequence), coronal plane (right), noncontrast study
-
Region:
- upper abdominal MR study, axial (left) and
- coronal (right) views
-
Radiologic sign:
- filling defect in the common bile duct
- Diagnosis: choledocholithiasis
24

- *Modality:**
- yellow → Sonogram of the appendix -linear 7,5–10 MHzprobe-
- Green → convex 3,5-5 MHz probe -B-mode-
- Red: power Doppler
- *Region:**
- Appendix
- longitudinal and cross-sectional views
- *Radiologic sign:**
- -yellow →* Small amount of free periappendiceal fluid is also present (yellow arrow).
- green → Thickened (more than 6 mm), non-compressible tubular structure
- -red arrow →* showing signs of edema and hyperVascularisation
Diagnosis:
Acute appendicitis