Images Flashcards
(79 cards)
Pt can’t recognize coin or paper clip placed in her right hands if her eyes are closed, but has no trouble w/ left hand
Called asteroagnosia
(a) Locate the lesion
(a) Parietal lobe/primary somatosensory cortex

Differentiate the 3 types of MRI


Dx

FInding = adenoma sebaceum = facial angiofibromas in characteristic butterfly pattern = pathognomonic for tuberous sclerosis
MRI findings of hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy (like alcoholic cirrhosis) => b/l, symmetric hyperintense lesions of the basal ganglia, most comonly in the globus pallidus

Dx

Hummingbird sign and Mickey Mouse sign both refer to midbrain atrophy seen in PSP (progressive supranuclear palsy)


Explain the concept of crossed findings seen in brainstem strokes
Crossed findings = ipsilateral CN findings (b/c CN don’t decussate) and contralateral sensory/motor findigns (corticospinal tract decussates caudally at medullary pyramids)
ex: lesion shown would give ipsilateral 3rd nerve palsy w/ contralateral motor/sensory deficits

MRI findings of pseudotumor cerebri
- slit like ventricles 2/2 compression by elevated ICP
- empty sella 2/2 pitutary flattening by elevated ICP



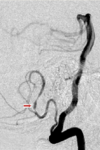
Name the vessels


Name ‘em




33 yo HIV+ F w/ low grade fever and HA x3 mo
- exam: cognitively slow, stiff neck
- LP shows 200 WBC
- CSF stain attached
(a) Dx
(b) Preferred Tx

(a) Cryptococcus neoformans = yeast that causes meningitis in immunocompromised, typically presents as lung infxn
(b) IV Amphotericin, then fluconazole

Name ‘em


Abduction vs. extension of the thumb
Adduction vs. flexion of the thumb




1 = anterior commisure
2 = lamina terminalis
3 = optic chiasm
4 = hypothalamic sulcus
5 = tuber cinereum
9 = infundibulum

Explain the vascular territories of the brain from the major arteries

What area of the brain is responsible for maintaining consciousness?

Reticular activating system (most influential component is the reticular formation): regulates wakefullness and sleep-wake transitions

P/w sudden inability to speak
After several days determine he can speak but only chooses to do so under extreme duress
(a) Dx
(b) Locate the lesion
(a) Akinetic mutism
(b) B/l cingulate gyrus = fold in brain superior to corpus callosum involved in emotiosn and regulation of aggressive behavior

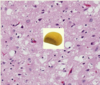
16 yo M p/w progressive muscle weakness, muscle biopsy below
Dx

Dx = mitochondrial myopathy
-biopsy: ‘ragged red’ muscle fibers = abnormal accumulations of mitochondria
Describe location of Wernicke’s area
Left superior temporal gyrus

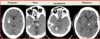
Describe the reversal sign on NCHCT and its indications
Reversal sign is when the cerebellum is brighter than the cortex parenchyma
-indicates no distinction btwn gray and white matter in the rest of the brain which is e/o global cerebral edema

45 yo F lost ability to recognize the face of her good friends
Locate the lesion
Prosopagnosia = inability to recognize known faces
Localizes to the fusiform gyrus of the temporal lobe- area for recognition
-color recognition, face recognition