Immunology and Immunopathology Flashcards
(99 cards)
Label the diagram.

- Pluripotent Stem Cell
- Common lymphoid progenitor
- Myeloid progenitor
- Megakaryocyte
- Platelets
- T-cell Precursor
- B-cell Precursor
- Natural Killer Cell
- B-cell
- Erythroblast
- Erythrocyte
- Neutrophil
- Basophil
- Eosinophil
- Monocyte
- Thymus
- T cell
- Macrophage
- Dendritic Cell
- Mast Cell
- Bone Marrow
- Periphery
- Blood
- T-dependant area of the lymph nodes and spleen
- B-cell areas of the lymph nodes, spleen, Peyer’s patches and tonsils
What product do pathogenic proteins produce?
bacterial toxins
What product do pathogenic small particles produce?
Viruses
What are the 6 fundamental immune responses against pathogens?
- Neutralisation of viruses and bacterial toxins by plasma proteins
- Ingestion & killing of pathogens by leucocytes (phagocytosis)
- Lysis of infected cells (cytotoxicity)
- Humoral response (complement + antibody)
- Containment of infected cells (granulomas)
- Cytotoxic lymphocytes
What cells are used in eliciting the innate immune response?
Cells used in the Innate Immune Response
- Mast Cells
- Dendritic Cells
- Marcophages
- γδT-cells
- Natural Killer Cells
- Basophils
- Eosinophils*
- Compliment protein*
- Neutrophil*
* all are granulocytes
What cells are used in the Adaptive Immune Response? (Be Specific)
Cells used in the Adaptive Immune Response
- B-cells = specifically the antibodies
- γδT-cells
- Natural Killer T-Cells
- T cells = specifically CD4+ & CD8+ (Thelper & Cytotoxic T cells)
What cells are used in both the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses?
- Natural Killer T cells
- γδTcells
What are the differences between the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses? (hint = should be 7 differences)
Innate
Adaptive
Naturally present
Produced after exposure to antigens
Present at birth
Develops during childhood
Rapid onset (hours to days)
Slow onset (days to weeks)
No specificity
Antigen specificity
No memory
Memory for antigens (B and T cells)
Limited diversity
High Diversity
Present in invertebrates and vertebrates
Present in vertebrates only
What is the humoral Immune response?
Humoral Immune Response
Innate & Adaptive immune responses mediated by soluble (cell-free) proteins in the plasma, interstitial fluids and mucosal secretions
What is the cellular immune response?
Cellular Immune Response
Is the innate and adaptive immune responses mediated by cells of the immune system (particularly effective against intracellular pathogens)
Label the diagram
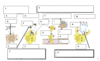
The Complement System
- Lyse Bacterial by forming MAC
- Tag Pathogens to enhance recognition and destruction by phagocytes opsonisation)
- Active inflammatory response by triggering the release of histamine from mast cells
- Enhance clearance of antigen-antibody complexes
A = Lysis
B = MAC = Membrane Attack Complex
C = Target Cell
D = Opsonization
E = Bacteria
E 2.0 = Phagocyte
F =Activation of inflammatory response
G =Complement Receptor
H = Extravasation
I = Mast Cell
J = Degranulation
K = Tissue
L = Blood
M = Clearance of immune complexes
N = Ag-Ab complex
O = Phagocyte
What are the different types of antigens in placental animals (i.e. Humans, sheep etc.)?
Immunoglobin types
- IgM
- IgD
- IgE
- IgG
- IgA
What the different types of immunoglobin types in birds?
Immunoglobin Types
- IgM
- IgY (with 2 different shapes)
- IgA
What are the different types of immunoglobin present in Amphibians?
Immunoglobin types
- IgM
- IgY (1 shape)
- IgX
What are the different types of immunoglobins present in bony fish?
Immunoglobin types
- IgM
- IgO
What are the different types of immunoglobins present in cartilaginous fish?
Immunoglobin Types
- IgM
- IgW (two different shapes)
- IgNAR
What are the different types of immunoglobins present in jawless fish?
hahah trick question they have none
Of the different classes of vertebral animals which are positive or negative to …
a. having DNA rearrangment, hypermutation & a thymus and spleen
b. Class switch
c. Germinal centre formation
(Classes are; 1 = placental mammals, 2 = birds, 3 = amphibians, 4 = Bony fish, 5 = Catilaginous fish & 6 = Jawless fish)
- Placental mammals
- a. +ive
- b. =+ive
- c. +ive
- Birds
- a. +ive
- b. +ive
- c. +ive
- Amphibians
- a. +ive
- b. +ive
- c. -ive
- Bony Fish
- a. +ive
- b. -ive
- c. -ive
- Cartilagous fish
- a. +ive
- b. -ive
- c. -ive
- Jawless fish
- a. ???
- b. -ive
- c. -ive
What do naive mature B-cells differentiate into?
a. Plasma Cells
b. Memory B cells
What is the function of plasma Cells?
Plasma Cells
- produces or secretes IgG, IgA, IgE but requires the help of T cells
- IgM can be produced by B cells independently of help from T cells
What is the function of memory B cells? What is the difference between long and short lived memory B cells?
Memory B cells
- express antibodies on their surface
- do not produce antibodies until a MAC or Ab-Ag complex is formed
- long lived memory B cells produce IgG, IgA or IgE but require help from the T cells
- short lived memory B cells only produce IgM (no T cell help)
What are the different types of cells in the formation of both memory B & plasma cells? (does the cell have any extra things? i.e. any antibodies)
- Stem Cell
- Progenitor B-cell
- B-cell Precursor
- Immature B = IgM antibodies
- Mature B = IgM & IgD and the first or primary antigen is presented to the cell
- Either forms
- a. Memory B cell
- b. plasma cell which has either IgM or (if T cell helps) IgG, IgA or IgE
- On second exposure to antigen the memory B cells act on plasma cells to elicit an immune response
What is the function of IgD immunoglobins?
IgD
- are produced by mature B cells
- fuse with the membrane during the exocytosis of the IgD antibody
- Are a primary B cell receptor
What is the function of the IgM immunoglobulin?
IgM
- is either monomeric or pentamer
- is one of the primary B cell receptors
- Are secreted by the Plasma Cells
- secreted in both the primary and second immune responses BUT higher % in primary
- Activate the complement complex (MAC) & opsonophagocytosis
- Cause agglutination



