Infection of Skin and Soft Tissue Flashcards
(26 cards)
Staphylococcus aureus causes what 4 skin infections?
- Folliculities
- Furuncles
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Bacteremia
Streptococcus pyogenes causes which six skin infections?
- Cellulitis
- Lymphangitis
- Impetigo
- Erysipelas
- Necrotizing fasciitis
- Toxic shock syndrome
Which enzymes affect spread and multiplication in skin infections?
- Hyaluronidase (spreading factor, Staph and Strep use as toxin)
- Hemolysins (destroys RBC)
- Lipases
- Collagenase
- Elastases
What are predisposing risk factors to exogenous skin infections from staph or strep?
- Excessive moisture
- Trauma
- Introduction of foreign body
- Pressure
- Compromised blood supply
What is the skin response to exogenous infections? (3)
-
spreading infections :
- impetigo- epidermis
- Erysipelas- dermal lymphatics
- Cellulitis- subcutaneous fat layer
-
abscess formation:
- folliculitis, furuncles/boils
- carbuncles
-
necrotizing infection
- Fasciitis and gas gangrene/myonecrosis
What organism causes gas gangrene?
Clostridia
Of staphylococci and streptococci which is catalase +?
Staphylococci
Which Staphylococci is coagulase (+) and (-)?
- (+): S. aureus
- (-):
- S. epidermidis (novobiacin sensitive)
- S saprophyticus (novobiacin resistant)
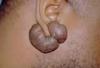
- Folliculitis is caused by which bacteria?
- What does it cause?
-
Staphyloccocus aureus
- infects sebaceous glands and hair follicles become inflamed
- There is an influx of neutrophils
- fibrin is deposited (site walled off) and an abscess is made
Furuncles/ Carbuncles are abscess is? Caused by what bacteria?
-
S. aureus
- Abscess in subcutaneous tissue
- Furuncle= single
- Carbuncle= Multiple, interconnected
- Abscess in subcutaneous tissue
Necrotizing fasciitis, myonecrosis and Gangarene are rapidly progressing? What toxin is produced/ which bacteria?
- Rapidly progressing cellulitis
- extensive necrosis of subcutaneous tissue (acute)
- Toxin producing Clostridium perfringens and S. pyogenes produce virulence factors (particularly M protein)
Symptoms of Necrotizing Fasciitis?
Intense pain, fever inflammation

- What kind of bacteria is Clostridium perfringens?
- What toxins does it produce?
- Gram positive bacilli (anaerobic)
- spore forming
- Toxins A-E
- Exotoxins: alpha toxin hydrolyzes cell membranes
- Phospholipase
- Hemolysins (destroy RBC)
- Collagenases
What are 3 cutaneous responses to bacterial toxins?
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Scalded fever syndrome
- Scarlet fever
Toxic shock syndrome is caused by which bacteria? MOA?
- Staphylococcus aureus producing toxins
- Binds to MHC and TCR outside of antigen binding site
- cause overwhelming release of IL-1,IL-2, INF gamma and TNF alpha
- —> shock
Symptoms of Toxic Shock syndrome?
- Multisystem involvement: shock, fever, rash
- desquamation (skin peeling)
- septicemia (infection in blood)
- toxemia
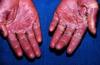
- Scalded Skin Syndrome is caused by which bacteria?
- MOA?
- Characterized by?
-
Staph. aureus
- exfoliation toxin producing (Exotoxin)
- exotoxin destroys keratinocyte attachments in stratum granulosum (separation of top layer of epidermis)
- Characterized by:
- fever
- generalized erythematous rash with sloughing of upper layers of epidermis

-
Ecthyma gangrenosum causes necrotic skin lesions
- caused by which type of bacteria?
- Typically seen in which patients?
- Toxins produced?
Pseudomonas aeruginosae;
- gram (-) rod that is oxidase positive
-
Opportunist pathogen
- typically seen in immune compromised patients
- Major nosocomial (in hospital) pathogen has multi drug resistance
-
Opportunist pathogen
Toxins:
- Endotoxin
- Exotoxin A (inhibitor of EF in eukaryotic protein synthesis)
- Extracellular slime Pigments
Mycobacteria are what kind of bacteria?
- Gram (+) cell wall
- Acid fast (mycolic acid)
- slow growing

- Mycobacterium terberculosis
- M. marinum
- M. ulcerans
All cause?
- All cause chronic ulcers
- M. terberculosis= TB
- M. Marinum= swimming pool
- M. Ulcerans= in tropical countries
Nocardia brasiliensis which is a bacteria that causes chronic ulcers is what kind of bacteria?
- Branching and intracellular opportunist
- Partial acid fast
- Beaded gram (+) bacilli
Main virulence factosr of Staph. aureus and Strep. pyogenes?
-
Strep. pyogenes:
- M protein
- exotoxins
- streptolysins S&O
- Streptokinas A&B
- hyaluronidase
-
Staph. aureus:
- Proteins A
- Capsule
- Coagulase
- Mucopeptide
- Where is the location of beta lactamases in bacteria?
- How are they resistance to antibiotics like penicillin?
- Beta lactamases are excreted into extracellular space by Gram (+) bacteria and into periplasmic space by gram (-) bacteria
- beta lactamase enzyme cleaves beta lactam ring rendering antibiotic ineffective
- Subcutaneous tissue connects?
- Composed of?
- Connects dermis to the deeper fascia
- has fascial layers (Scarpa’s and Camper’s)
-
Composed of:
- loose connective tissue
- stored fat (thickness varies greatly)
-
Contains
- vessels
- nerves
- glands