Infectious Disease Flashcards
(267 cards)
Drug of choice for Syphilis

Penicillin G

When you see Gram(+) cocci in clusters, what do you cover for?
MRSA
Treatment of choice for MRSA?
Vancomycin
Best antibiotic for Methicillin-Sensitive Staph Aureus?
Cefazoline
What bacteria to consider when seeing Gram(+) cocci in pairs and chains?
Streptococcus
Gram(+) bacilli seen in gastroenteritis and meningitis?
Listeria
Tx of choice for Bacillus anthracis?
Ciprofloxacin
Tx of choice for Actinomyces?
Penicillin
What organisms do Cephalosporin NOT cover?
LAME
- Listeria
- Atypicals
- MRSA (except Cefazoline)
- Enterococcus
What is Catalase positive, Coagulase positive cocci?
Staph Aureus
What are alpha-hemolytic Streptococcus?
Strep pneumo and Viridans
What are beta-hemolytic Streptococcus?
S. pyogenes and S. agalactiae
What are gamma-hemolytic streptococcus?
Enterococcus
What type of cocci is Enterococcus?
Gram positive in pairs and chains.
Enterococcus is not covered by ________.
Cephalosporins
Best Tx for group A strep
Penicillin
What anaerobes are resistant to penicillin?
Bacteroides spp.
How does actinomyces present?
Abscess in the mandible, oral lesions
Tx of choice for Listeria?
Ampicillin
What do you need to treat Staph aureus?
Beta lactamase inhibitors + Penicillins
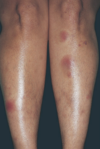
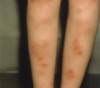
When covering for cellulitis, you cover for what organisms?
Group A strep (pyogenes) and MSSA
Tx of choice for cellulitis
1st gen cephalosporins
Examples of 2nd gen cephalosporins
Cefoxitin and Cefotetan
The only cephalosporins that treat for anaerobes?
2nd generation cephalosporins:
Cephamycins:
- Cefoxitin
- Cefotetan