Jen's "to know" Flashcards
(112 cards)
Decreased alb, decreased glob, decreased antithrombin
Protein losing enteropathy

MAP Struvite
T/F hypoalbuminemia can be due to diet
TRUE- intake vs need
What casts are never normal
Epithelial cellular casts
Fanconi- glucose findings
Glucosuria but not hyperglycemia
When are fatty casts seen
cats, schnauzers, diabetes, nephrotic syndrome, any hyperlipidemic animal

Ammonium biurate
Golden to brown spheres with irregular protrusions
Rare normal in dalmation, bulldogs
Liver failure, sago palm
When are hemoglobin casts seen
Hemoglobinemia and intravascular hemolysis
Protein plasma concentration -age
Neonates low albumin, low globulin until colostrum
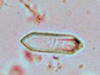
Calcium oxalate monohydrate
ethylene glycol poisoning

Caudate epithlium
When is the ability to concentrate urine lost
66% nephron function loss
Polyclonal gammopathy
Wide, blunted SPE peak; likely infection or antigenic stimulation

pseudo casts

Squamous epithelium

NMB fungal aspergillosis
Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate - cause
Eating plants, can be normal (di- two lines crossing)

Transitional epithelium
Effect of rapid fluid replacement after hemorrhage
hypoproteinemia and anemia

Epithelial (cellular) casts

lipid droplet
What type of APP - albumin
Negative

Wazy cast

Fatty cats (normal in cats, animal with hyperlipidemia