Kidney Cysts- MJ Flashcards
(59 cards)
T/F: you can get renal cyst development in the following ways:
- Genetic and non-genetic processes (autosomal dominant PKD)
- Variety of childhood and adult diseases (Acquired renal cysts 2° to chronic renal failure)
True
What are the 5 ways renal cysts are categorized?
- Size
- Location
- Spetations
- Calcifications
- Contents
- Enhancement
65-70% of renal masses are what?
simple renal cyst
Simple renal cysts are frequently observed in normal kidneys. What age group is it least common to see these in and what group is it most common?
- Least common: 15 to 29 years – 0% males & 0% females
- Most common: >70 years – 32% males & 15% females
T/F: Simple renal cysts are the most common incidental finding
True
T/F: a patient that is found to have a simple renal cyst has a much higher risk of HTN, CA, CKD or ESRD
FALSE
Simple renal cysts have little clinical significance
Where do simple renal cysts develop?
Are they usually solitary or multiple?
Unilateral or bilateral?
- Develop In the cortex of the medulla
- Can be solitary or multiple, unilateral or bilateral- varies greatly in size and shape
- Is obstruction, rupture, infection (renal abscess) and HTN caused by a simple renal cyst common or rare?
- What would be the sxs of rupture of infection?
Rare
- Sxs:
- Rupture= flank pain, hematuria
- Infection= fever, vague lumbo-abdominal pain, +/- hematuria/pyuria
What is the main goal for evaluating someone with a simple renal cyst? What is the first line diagnostic study for this?
- Goal is to distinguish simple cysts from complex cysts
- U/S is first line
What are the 3 ultrasound criteria for simple cysts?
- Sharply demarcated w/ smooth thin walls
- No echoes (anechoic) within the mass
- Enhanced back wall indicating good transmission through the cyst
What are the 5 ultrasound characteristics of complex cysts?
- Thick walls and/or septations
- Calcifications
- Solid components
- Mixed echogenicity
- Vascularity
Evaluation of Simple Renal Cyst:
If US is equivical or is consistent w/ complex cyst, what diagnostic study should be ordered next?
CT w/ and w/o contrast
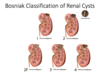
Bosniak Classification of Renal Cysts: Which category?
- CT features:
- sharply demarcated w/ smooth thin wall
- homogenous fluid
- no contrast enhancement
- Significance:
- Simple cyst
- benign
- image in 6-12 mo
Category I

Bosniak Classification of Renal Cysts: Which category?
- CT features:
- Closely resemble simple cysts
- Few thin septa
- +/- few calcifications
- < 3cm
- well marginated
- No enhancement
- Significance:
- Complex cyst
- benign
- image in 6-12mo
Category II

Bosniak Classification of Renal Cysts: Which category?
- CT features:
- Multiple thin septa
- Walls may be thickened and may contain calcifications
- > 3cm
- Significance
- Complex cyst
- likely benign (5% malignant)
- repeat imaging in 3-6mo
Category IIF

Bosniak Classification of Renal Cysts: Which category?
- CT Features:
- Indeterminate cystic masses
- Thickened irregular walls or septa
- measurable enhancement
- Significance
- complex cyst
- 40-60% are malignant
- monitor or excise
Category III

Bosniak Classification of Renal Cysts: Which category? What is the significance of this type of cyst?
- CT features:
- Indeterminate cystic masses
- thickened irregular walls or septa
- measurable enhancement
- Soft-tissue enhancing
- complonents adjacent to cyst wall
Category IV
significance: Complex cyst, 85-100% are malignant
What are the two major causes of acquired renal cysts? Which one is most common?
- Chronic Renal Failure (MC)
- Dialysis (incidence increases w/ duration)
What is the diagnostic criteria for acquired renal cysts? (3)
- Bilateral involvement
- > 4 cysts
- Diameter rangin from <0.5cm up to 2-3cm
In patients with acquired renal cysts, what size are the kidneys typically?
small to normal in size
Acquired Renal Cysts:
Are patients usually symptomatic or asymptomatic?
What is the clinical significance of these cysts?
- Rarely symptomatic
- Clinical significance= may increase RCC risk
When should you consider screening patients for acquired renal cysts? What should you screen with?
- Yearly screening after being on dialysis for 3-5 years
- US vs CT w/ and w/o contrast (depending on what initial study shows)
What is the treatment for simple/complex renal cysts?
- Excision based on Bosniak Classification (usually not excised b/c benign)
- Acetaminophen or NSAID (if nml kidney funct) if having acute/intermittent pain



