Kidney Water Flashcards
(345 cards)
Benign tumors of the kidney
List 3
Renal papillary adenoma
Angiomyolipoma
Oncocytoma
Malignant tumors of the kidney
List 3
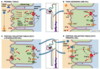
Renal cell carcinoma
Wilms tumor
Urothelial (transitional cell) carcinoma of renal pelvis
Renal Papillary Adenoma
Benign or Metastatic?
Gross Pathologic features (3):
Microscopic features (3):
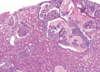
Benign
Gross: Small (<1.5cm); Pale, yellow gray, Discrete, well circumscribed.
Micro: Papillary or tubular architecture; bland nuclei, no atypia, No fibrous capsule or desmopastic response

Angiomyolipoma
Benign or Metastatic?
Gross Pathologic features (3):
Microscopic features (3):
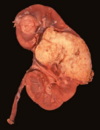
Benign
******Associated w/ tuberous sclerosis
patients may present w/ spontaneous hemorrhage
Gross: Tan to brown; Often yellow fat content; focal hemorrhage
Micro: Blood vessels; Smooth muscle; Adipose tissue

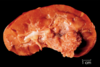
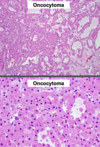
Oncocytoma
Benign or Metastatic?
Gross Pathologic features (4):
Microscopic features (3):

Benign
Gross: Well circumscribed; Homogenous; “Mahogany brown” color; Centra; stellate scar; Can be large (12cm)
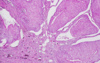
Micro: Cells arranged in nests; Eosinophilic (High [mit.]); Bland/round nuclei
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Begnin or Malignant?
Pathophysio to why this is dangerous?
3 Treatments (think based on size)
Malignant
****85% primary renal malignancies
Orgin in renal cortical tubules –> metastases –> lung/bone
Txt: Partial nephrectomy; Radical nephrectomy (whole kidney); Adjunct chemotherapy (VEFG/tyrosine kinases)
Renal Cell Carcinoma survival rate depends on?
What are 3 ways to classify RCC?
Depends on stage
Avg = 5 yrs
Kidney - 95%: Distant metastases - <10%
Clear cell; Papillary; Chromophobe
What specific chromosomal abnormalities lead to Clear-cell type and Papillary type RCC?
Explain pathopsio of each
Clear-cell: Deletion Chromosome 3p (VHL gene) –> Loss of tumor suppressor gene –> promotes tumor angiogenesis thru VEGF
Papillary: Trisomy Chromosome 7 –> mutation of MET proto-oncogene (encodes tyrosine kinase receptor)
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Age it generally affects?
Gender?
Classic triad of symptoms (3):
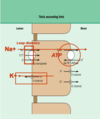
What does RCC secrete as a tumor?
Adults > 50yo
Males > Females
- Costovertebral angle pain
- Palpable mass
- Hematuria (most common symptom)
Polycthemia: Paraneoplastic syndrome; due to secretion of erythropoietin by tumor cells.

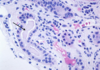
Renal Cell Carcinoma

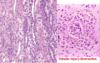
Clear Cell RCC
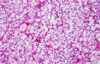
Clear Cell RCC

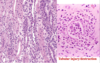
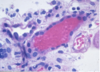
Papillary RCC

Papillary RCC

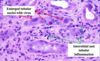
Chromophobe RCC
Grade of RCC


Pattern of RCC spread
- thru what gross structures of kidney and in the body?
Invasion through renal capsule into perinephric fat
Invasion into renal vein w/ proximal spread along inferior vena cava
Lymph nodes
Distant mets: lungs, bone

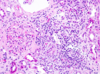
Wilms tumor (Nephroblastoma)
Begnin or malignant
age
Chromosome affected
what 2 syndromes is associated w/ this
Malignant
2-5yo
Mutation of WT1 gene on short arm of Chromosome 11
Associated w/ WAGR syndrome: Wilms tumor, Aniridia (absent iris), Genital anomalies, mental Retardation & Denys-Drash (Wilms tumor, gonadal dygenesis, early-onset nephropathy w/ renal failure)
How does Wilms tumor clinically present?
What does prognosis depend on?
presents as abdominal mass and abdominal pain; hematuria, intestinal obstruction, hypertension; 5-10% bilateral
.
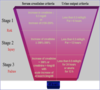
Prognosis depends on the degree of anaplasia of the tumor cells (defined by pleomorphism, hyperchromatism, abnormal mitoses), and the stage of the tumor at time of resection. Anaplastic tumors are more aggressive.
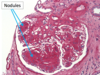
Gross pathologic features of Wilms tumor?
Nodular
Gray to tan-white
Soft, friable, fleshy

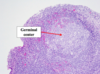
Wilms tumor Microscopic features (3)
- Triphasic pattern*
- Primitive blastema (small/dark undifferentiated cells)
- Epithelial component (abortive tubules/glomeruli)
- Stroma (Fibrous or myxoid patterns; may contain mesenchymal elements (cartilage, muscle, bone)

Wilms tumor microscopic features (3):
Triphasic pattern
- Primitive blastema (small/dark undifferentiated cells)
- Epithelial component (abortive tubules/glomeruli)
- Stroma (Fibrous or myxoid patterns; may contain mesenchymal elements (cartilage, muscle, bone)
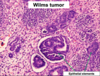

Wilms Tumor
What is the significance of this in WIlms Tumor?
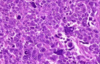
ANAPLASIA
Determines the Prognosis of Wilms tumor
- Pleomorphism, hyperchromatism, abnormal mitoses –> more aggresssive; higher resistance to chemotherapy
- Stage matters also w/ Prognosis*