L10: Pathologies and surgical management of cervical spine disorders Flashcards
(32 cards)
What are the 3 causes of neck pain (alone)?
- musculoligamentous
- discogenic pain
- facet osteoarthritis
What are the 3 treatments of neck pain (alone)?
- surgery ineffective
- best treated nonoperatively
- can consider facet injections
What is the bone scan VS SPECT VS SPECT-CT?

What is the cervical facet joint injection?
Put a needle down on the region of interests, which is where the small nerve roots come that supply the facet joints.
interrupting the pain pathways and the needle has a radio frequency current and you zap the nerve.
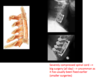
What are the 2 causes (groups) of radiculopathy?
- disc protrusion
- facet & uncovertebral OA with osteophytes
What are 4 presentations of radiculopathy?
- pain
- neck
- trapezius/medial scapula
- arm
- parasthesia
- weakness
- reflex loss
C5-6: trapezius pain
C6-7: levator scapula & rhomboid pain
Where does C5, C6, C7 get compressed? (What is the most common?)
C6 gets compressed at C5-6 level (most common) –> numbness of thumb, biceps weakness & reflexes
C7 gets compressed at C6-7 level (2nd most common) –> middle finger, triceps weakness & reflexes
C5 gets compressed at C4-5 level (rare)
What does a compressed exiting nerve root by disc herniation VS osteophytes (occur at the side, not the back)?
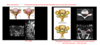
What are the 2 types of treatment of radiculopathy?
- non-operative
- operative
What are 2 non-operative treatments for radiculopathy?
- time
- nerve root block
What are 2 operative treatments for radiculopathy?
- can be treated ANTERIORLY with discectomy and fusion
- can be treated POSTERIORLY with foraminotomy

______ (Do not/do) exercise with disc herniation = will aggravate pain/get worse
Do not
What is the aim of spinal fusion?
Take nerve pressure but sacrifice movement at that level
- Doesn’t move much anyways
What does a disc replacement look like?

What does a disc replacement look like in a spinal x-ray?

What are the 3 causes of cervical myelopathy?
- DEGENERATION
- ISCHAEMIA
- PREDISPOSITION
What is degeneration in cervical myelopathy?
Unable to extend neck (narrower/compressed spinal canal) –> arm pain

What is predisposition in cervical myelopathy?

What is ischaemia in cervical myelopathy?
compression of anterior spinal artery important in early stages
What are the 7 symptoms of cervical myelopathy?
- Clumsy weak numb hands
- Leg stiffness or weakness
- Neck stiffness
- Pain in shoulders or arms
- Unsteady gait
- Urinary hesitancy
- L’Hermitte’s sign
vague slow delay
What is OPLO?
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
What are the 7 signs of cervical myelopathy?
- Wasting of hand intrinsics
- Hyperreflexia
- Hoffmann’s sign
- Variable sensory loss
- Inverted radial reflex
- L’Hermitte’s sign
- Cervical flexion cause tingly sensation down body
- Upgoing plantar response
- Ankle clonus
What are 3 gradings for Ranawat?
- Normal
- Subjective weakness with hyperreflexia & dysesthesia
- Objective weakness and long tract signs
- can ambulate
- cannot ambulate