Laboratory Equipment Flashcards
(31 cards)
What is the function of the Microscope?

Enable vision of elements that are too small to be seen with the naked eye
Microscopy
Inspection with magnification
Macroscopy
Gross inspection with the naked eye
What objects can be identified with microscopy? - CELLS
CELLS Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Sperm Platelets Looking at ratio and identification
What objects can be identidied with microscopy? - URINE
URINE Bacteria Casts Crystals
What objects can be identified with microscopy? PARASITES
PARASITES Worm eggs Lice Mites
Microscope elements Eye Piece

MONOCULAR BINOCULAR TRINOCULAR Eye piece holds the occular lense. Magnification of x10
Microscope elements Nose Piece

Lower end of the body tube Holds the objective lenses Rotate clockwise - LOWER - HIGHER
Microscope elements Objective Lenses

Housed in the nose pieces x4 - scanning x10 - low power x40 - high dry x100 - oil immersion
Total magnification
Objective lens x Eye piece e.g. 40 x 10 = x400
Microscope elements Limb / Arm

Connects the base with the body Supports the stage and condenser
Microscope elements Stage

A flat platform oh which the slide is placed. A hole in the centre allows light from the condenser to illuminate the specimen Stage can be moved up and down by the course and fine adjustment knobs.
Microscope elements

Mechanical stage
Attached to the stage, holds the slide in place as well as allowing movement of the slide up and down and side to side by using the mechanical stage hand wheel.
Microscope elements

Vernier scales
Scales that allows the relocation of a certain point of the slide.
Microscope element

Substage condenser
Below the stage Consists of two lenses that condense the light from the light source onto the specimen to make it brighter and the image sharper.
Microscope elements
Iris diaphragm
adjusting the aperture of the iris diaphragm with the control can regulate the amount of the light that passes through the condenser
Microscope elements
Base
Houses the light source houses on/off switch
Microscope elements

Rheostat
changes the intensity of the light
Battlement technique
the technique of looking at the body of a slide thoroughly. Start left-hand side

Define - Supernatant
Fluid from a spun sample
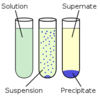
Define - Sediment
Solid from a spun sample

Functions of a centrifuge
Seperates sample Serum - cells from fluid PCV - cells of different densities Urine - concentrating material (sediment)
Spinning speeds Blood
10,000 RPM for 5 mins
Spinning speeds Urine
2,000 RPM for 5 mins


