Lect 12 Flashcards
(61 cards)
lobar pneumonia
involvement of the entire lobe
what is PNA
inflammation of the lung parenchyma

causes of PNA in people with no known predisposing factors
- mycoplasma pneumoniae
- streptococcus pneumoniae
- chlamydophila pneumoniae
causes of PNA in alcoholics/vagrants
- streptococcus pneumonia
- klebsiella pneumoniae
causes of PNA in people with underlying disease
- streptococcus pneumoniae
- H. influenzae
- pseudomonas aeruginosa
- staph. aureus
causes of PNA in people with persons requiring ventilation
- klebsiella pneumoniae
- pseudomonas aeruginosa
causes of PNA in people with travel/occupational exposure
Legionella pneumophila
what is 6th leading cause of death and most common infectious cause of death
PNA
- mortality rate is 25% in infections requiring hospital admission
PNA can be divided into what two groups
- hospital acquired (Nosocomial)
- develops 72 hours or more following admission
- community acquired (CAP)
- develops in people with limited or no contact with medical settings
community acquired PNA can be divded into what two groups
- typical vs atypical
typical CAP involves infection from which organisms
- S. Pneumoniae
- H. influenzae
- K. pneumoniae
- S. aureus
atypical CAP involves infection from which organisms
- zoonotic
- nonzoonotic
- chlamydia pneumoniae
- mycoplasma pneumoniae
- legionalle pneumoniae
- usually have extrapulmonary involvement and cause systemic infections
what types of ABx will not work against atypical PNA
- PCN because atypical PNA are unresponsive to B-lactams
clinical presentation
- sudeen onset
- sick appearance
- high temperature (>103)
- productive cough
- pleurisy
- consoldiation on CXR
- CP, SOB
typical bacterial PNA
clinical presentation
- gradual onset
- well appearance
- lower temperature <103
- non productive cough
- patchy infiltrates on CXR
- diarrhea, abd pain
atypical bacterial PNA
streptococcus pneumoniae
- gram status
- shape
- gram positive
- lancet shaped diplococcus
streptococcus pneumoniae: typical presentation on blood agar plate
-
alpha hemolytic colonies
- green colored colonies
when does streptococcus pneumoniae occur (season)
occurs more colder, wetter months
streptococcus pneumoniae incidence is in what patient populations
- young children
- adults > 65 yo
reervoir for streptococcus pneumoniae
asymptomatic carriers
streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factor (capsule)
- capsule
- inhibits phagocytosis
- interferes with complement activity
- prevents C3b opsonization of the bacteria

streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factors (seen in gram positive bacteria)
- peptidoglycan-teichoic acid complex
- illicits a significant immune response
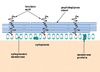
virulence factor specific to streptococcus pneumoniae
- Pneumolysin
- interacts with target cell membrane
- forms transmembrane pores
- results in cell lysis
- activates complement
streptococcus pneumoniae virulence factor: autolysin
- causes lysis of pneumococcus and results in release of pneymolysin and release of other virulence factors
- in response to antibiotic therapy and stationary phase
- attempt by organism to dampen host immune response by overwhelming it