Lecture 2 - Gross Anatomy (HARC 1) Flashcards
(35 cards)
Function of Kidney
1.) Excrete waste products of metabolism as urine 2.) Water and electrolyte balance in the body 3.) Maintain acid-base balance of blood
What is the peritoneum?
A continuous transparent membrane which lines the abdominal cavity and covers the abdominal organs (or viscera).
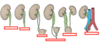
Where do the kidneys sit?
Lie behind peritoneum high on posterior abdominal wall either side of the vertebral column
Why is the right kidney lower?
Liver
Which ribs cover left kidney?
Ribs 11 and 12
Which ribs cover right kidney?
Rib 12




What is a renal calyx?
- Calyces are chambers of the kidney through which urine passes
- Minor calyces surround the apex of the renal pyramids.
- Two or three minor calyces converge to form a major calyx


Flow of Urine
Collecting Ducts → Minor Calyx → Major Calyx → Renal Pelvis → Ureter
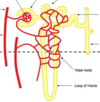

Glomerulus
- Tuft of capillaries
- Blood enters via afferent arteriole
- Leaves via efferent arteriole
- Plasma filtrate passes over B’s C epithelium and enters proximal tubule.
- Controlled by juxtaglomerular cells (smooth muscle)


Kidney Blood Flow

Urine Formation
- Filtration
- Reabsorption
- Secretion
- Excretion
How much fluid do kidneys filter every day?
180 Litres
How much of filtrate is reabsorbed in PCT and Loop of Henle?
Over 70%
What solutes are actively transported out of PCT?
Glucose, Amino Acids, Bicarbonate
Where is Sodium reabsorbed?
PCT (60%), Loop of Henle (30%), DCT (10%)
Roughly
What is Vasopressin?
Antidiuretic Hormone
(Increases DCT and Collecting Duct permeability to water)
Secretion
- Post filtration, kidney continues to secrete additional substances into tubular fluid.
- Enhances kidney’s ability to eliminate certain toxins and wastes.
- Essential to plasma concetrations and pH.
Excretion
Final composition of urine
Ureter
Carries urine from renal pelvis to bladder