Lecture 20 - Female Reproductive System Flashcards
(38 cards)
Gonads
both systems have primary sex organs called gonads
• produce sex cells called gametes
- > Oocytes in females
- > sperm in males
• both systems have ducts to transport gametes from gonads to site of fertilization
Perineum
diamond-shaped region between thighs with the following boundaries:
- > pubis symphysis
- > ischeal tuberosities
- > coccyx
Subdivided into…
- Urogenital triangle
- Anal triangle

Urogenital triangle vs Anal triangle
Urogenital triangle
- > anterior
- > ischial tuberosities and pubis symphysis
Anal Triangle
- > posterior
- > ischial tuberosities and coccyx

Primary vs Accessory female reproductive organs
Primary
- > ovaries
Accessory
- > Uterine/fallopian tubes
- > uterus
- > vagina
- > mammary glands
Pouches of female reproductive system
*formed from peritoneal folds around pelvic organs*
- Vesicouterine pouch
- > anterior space between the uterus and urinary bladder - Rectouterine pouch
- > posterior space between the uterus and the rectum

Anchoring ligaments of the ovaries; how is it anchored within the pelvic cavity
*anchored within pelvic cavity by several folds of peritoneum*
- Broad ligament
- Ovarian ligament
- Suspensory ligament

Structures/layers of the ovary
- > each ovary is surrounded by an epithelial layer of simple cuboidal cells called the germinal epithelium
- > deep to the GE is a connective tissue capsule called the tunica albuginea
- > deep to TA, the ovary can be divided into an outter cortex and an inner medulla

Cortex and medulla of the ovary
- > the cortex contains ovarian follicles
- > medulla contains connective tissue, blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves

Ovarian follicles
- > thousands are found within the cortex of ovary
- > OF consist of oocytes surrounded by follicle cells
- > several different types of ovarian follicles, each representing a different stage of development
Stages of follicle development
- Primordial follicle
- Primary follicle
- Secondary follicle
- Vesicular follicle
- Corpus luteum
- Corpus albicans
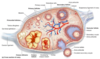
Primordial follicle
- > most primative type
consists of…
- > a primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of squamous cells

Primary follicle
consists of..
- > primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal cells
Secondary follicle
consists of…
- > a primary oocyte, many layers of granulosa cells and a fluid-filled space call an antrum
- > 2 protective structures surround the primary oocyte
* Zona pellucida (outside)
* Corona Radiata (inside)
* antrum

Antrum
contains serous fluid that increases in volume as ovulation nears
- > protective/nutritional fluid
Protective structures surrounding the primary oocyte
- Zona pellucida (outside)
- Corona Radiata (inside)

Vesicular follicle
aka. mature follicle or Graafian follicle
consists of…
- > secondary oocyte surrounded by zona pellucida and corona radiata
- > an enlarged antrum
- > many layers of follicle cells
- > walls of follicle merges with ovarian wall and eventually releases the follicle into a uterine tube

Corpus luteum
- > following ovulation, the remnants of the follicle (not including the oocyte) becomes the corpus luteam
- > CL secretes progesterone and estrogen, which stimulate the growth of the uterine endometrium

Ovulation
- > the membrane of the vestibular follicle fuses to the ovarian membrane
- > the follicle ruptures and releases the oocyte into the fimbrea/uterine tube
Corpus Albicans
- > corpus luteum degrades itself into the corpus albicans
- > the corpus albicans is scar tissue that doesn’t secrete anything (estrogen or progesterone)

Characteristics of uterine tubes and oocyte travel
- > extends laterally from both sides of the uterus
- > around 10-12cm in length
- > covered in mesosalpinx (part of broad ligament)
- > the secondary oocyte is usually fertilized in the lateral part of fallopian tube (pre-embryo)
- > takes the pre-embryo around 3 days to travel the length of uterine tube and reach the lumen of the uterus
Regions of the uterine tubes
Infundibulum - > lateral opening of the tube, encircled by fimbriae (fingers)
Ampulla - > expanded region medial to infundibulum where fertilization typically occurs
Isthmus - > medial to the ampula and represents 1/3 of the entire length of UT
Uterine part - > contiuous with the uterus

Walls of the uterine tubes
- Mucosa - > cilliated (movement) columnar epithelial cells
- Muscularis - > innter circular layer and outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle
- Serosa - > external serous membrane covering uterine tube
*no submucosa - > does not need to secrete anything*

Characteristics of uterus
- > pear-shaped, thick-walled muscular organ within pelvic cavity
- > possesses a lumen that is superiorlaterally continuous with the uterine tubes and inferiorly contiuous with vagina
functions of uterus
- > site of implantation
- > supports and protects the developing embryo/fetus






