Lecture 4: Hyperchloremic Acidosis (aka Non-anion gap) Flashcards
(38 cards)
A pH < ____ is considered acidosis
pH < 7.36
In urine studies what is the primary unmeasured anion?
NH4
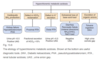
How do you calculate urine anion gap (UAG)?
UAG = [Na+ + K+] - [Cl-]
When Cl- > Na+ + K+ the urine anion gap is negative and indicates what about NH4+ and the cause of the acidosis?
NH4 is appropriately secreted and suggests non-renal cause for acidosis
When urine anion gap (UAG) is positive, what does this suggest about the cause of the acidosis?
Renal cause
Major presenting sx’s of pyelonephritis w/ obstructive uropathy?
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Foul smelling urine
- Renal colic
Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis due to inadequate NH3 production, caused by renal failure, hypoaldosteronism, or pseudohypoaldosteronism will have what urine pH and UAG finding?
- Urine pH <5.5
- Positive UAG

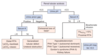
A fractional excretion of HCO3 > 15% leading to hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis is due to what disorder?
Proximal RTA = type 2

Which urine pH and UAG finding is associated with distal RTA = type 1?
- Urine pH >5.5
- Positive UAG

What are 5 disorders causing extrarenal loss of base acid load and are associated with a negative UAG?
- Diarrhea
- Pancreatic fistula
- Ureteral diversions
- NH4Cl/HCL
- NaCl load
What are 2 causes of hyprchloremic metabolic acidosis that will have a high urine osmole gap?
- Toulene ingestion
- DKA

What type of RTA is associated with a urine pH >5.5, positive UAG, and hypokalemia?
Distal RTA = type 1

RTA with urine pH >5.5, positive UAG, and hyperkalemia can be due to what 2 disorders?
- Generalized tubular defect
- Ureteral obstruction

Which type of RTA is associated with positive UAG and hyperkalemia?
RTA type 4

What are 5 major causes of RTA type 4?
- Hypoaldosteronism
- PHA type 1 (AD)
- PHA type 1 (AR)
- Gordon’s syndrome (PHA II)
- Kidney failure
Which type of RTA is associated w/ hyperkalemia and positive UAG?
Proximal RTA = type 4

Major urine findings of RTA type 2 (aka proximal RTA)?
- Glycosuria
- Aminoaciduria
- Phosphaturia
- Bicarbonaturia
Classic distal RTA type 1 is an inability of the distal tubule to?
Acidify the urine

Classic distal RTA type 1 is associated with what 3 drugs?
- Lithium
- Toluene
- Amphotericin

Pts with RTA type 1 (aka classic distal) have hypocitraturia and hypercaliuria so they are prone to what?
- Nephrolithiasis = calcium oxalate stones
- Nephrocalcinosis
- Bones problems —> rickets (children) and osteoporosis/malacia (adults)
Which type of RTA has decreased ammoniagenesis due to hyperkalemia?
RTA type 4 (hypoaldosteronism)
Due to the low aldosterone in RTA type 4 there is less Na+ reabsorbed and the lumen is less negative, so how is the pH maintained at a normal level?
Hydrogen pump is still effective

RTA type IV is made worse by which drugs?
- Drugs affecting RAAS: ACE inhibitors, ARBs and NSAIDs
- Especially K+-sparing diuretics (i.e., amiloride, triamterene, and spironolactone)
RTA type IV is usually a presumptive diagnosis and must be proven by what 2 levels?
Low renin and low aldosterone







