Lecture 8 Flashcards
(35 cards)
What does Wilhelmy show in 1850?
Rate of acid hydrolysis of sucrose is proportional to sucrose concentration at constant acid concentration.
In 1902, what does Brown find?
There are different kinetics for the same reaction catalysed by invertase. At low sucrose concentrations, rate proportional to sucrose concentration, but independent at high sucrose concentrations.
Enzymes become saturated by substrate at higher substrate concentrations. What is the only way to increase reaction rates? Furthermore, what is this used as evidence for?
Add more enzyme. Evidence for formation of discrete enzyme substrate complex intermediate between substrate and products.
What did Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten do and when?
Provided mathematical solution describing rectangular hyperbolic nature of rate vs [substrate] plot. 1913.
What is the Michaelis Menten equation?

What is KM?
What does it mean?
The Michaelis constant.
Means the concentration of Substrate ([S]) at half Vmax.
What is Vmax?
Maximum rate of reaction.
What is the equation showing the equilibrium between Substrate and Product?
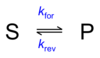
What equation forms the original basis of which the Michaelis Menten equation was developed?
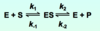
What is assumed about k2?
It is a negligible rate, therefore happening in the forward direction only.
What is the unit used for KM?
M.
What does KM represent in terms of the amount of enzyme occupied?
Represents the substrate concentration at which the rate (and therefore the number of active sites occupied) is half maximal.
What does KM often approximate the affinity of?
The enzyme to the substrate.
What does a low value for KM mean for the affinity of the substrate?
High affinity, i.e. strong/tight binding.
In many cases, what is the in vivo substrate concentration close to?
The value for KM.
Why is KM a constant?
Because it defines the interaction between enzyme and substrate molecules.
What is KM independent of?
Amount of enzyme and substrate present.
Is Vmax a constant? Why?
No.
Measured value only applies to one particular reaction condition.
Will adding more enzyme increase KM and Vmax?
Will increase Vmax but not KM.
When is Vmax reached? And can this be done in practice?
When all substrate binding sites are full.
No, only theoretical.
What is the turnover number?
And what’s the units?
Number of substrate molecules converted into product per unit time when the enzyme is fully saturated with substrate.
s-1.
What does the turnover number mean in real terms?
The efficiency of the enzyme.
What symbol can be used to describe the turnover number?
kcat.
What 2 things is kcat equal to?
Kinetic constant k2.
Vmax/amount of enzyme.


