Lecture Review Flashcards
(161 cards)
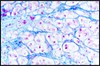
What parasite is this image associated with?

Babesia
(presence of tetrad)
What specific parasite is this associated with?

Plasmodium Falciparum
(Banana gametocyte)
ID the parasite this image is associated with

Acid fast of Cryptosporidium oocysts
ID the parasite this image is associated with

Fluoresence of Cryptosporidium Oocysts
What parasite is this?

Giardia
What organism is this associated with?
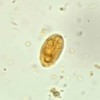
This is a cyst for Giardia

Trichomonas Vaginalis
What is this and what is it associated with?

Amastigote
Intracellular form of Leishmania/Trypanosomiasis found in human
This is the result of what?

Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
What is this from?

DFA (fluoresence) of Pneumocystis Jiroveci (Carinii)
What is this?

Silver Stain of Pneumocystis Jiroveci (Carinii). Shows empty cysts which have expelled the protozoa.
Interpret this Serology:
HBsAg: negative
anti-HBc: negative
anti-HBs: negative
Susceptible
Interpret this Serology:
HBsAg: negative
anti-HBc: positive
anti-HBs: positive
Immune due to natural infection
Interpret this Serology:
HBsAg: negative
anti-HBc: negative
anti-HBs: positive
Immune due to hepatitis B vaccination
Interpret this Serology:
HBsAg: positive
anti-HBc: positve
IgM anti-HBc: positive
anti-HBs: negative
Acutely infected
Interpret this Serology:
HBsAg: positive
anti-HBc: positve
IgM anti-HBc: negative
anti-HBs: negative
Chronically infected
Interpret this Serology:
HBsAg: negative
anti-HBc: positve
anti-HBs: negative
Interpretation unclear! (4 possibilities)
- Resolved infection (most common)
- False positive anti-HBc (thus susceptible)
- “Low level” chronic infection
- Resolving acute infection
What liver disease is this associated with?
(hint: these are plasma cells)
What else might you see?

Autoimmune hepatitis
This image shows plasma cells creeping into the lobule. You would also expect to see interface hepatitis.
Positive blue staining for iron in liver as in the image, is indicative of what disease process?

Hemochromatosis
A disease of iron overload
What is the phenomenom in the bottom left photo called and what is it associated with?

“Scalloped edges”
Celiac Disease
What is pyloric stenosis and what are its symptoms (3)?
Congenital hypertrophy of the smooth muscle of the pylorus
Sx: projectile vomiting in first 2-6 weeks of life, visible peristalsis, olive-like mass in abdomen.
What is the most likely cause for acute gastritis? chronic?
acute: impairment of protective system (via NSAIDs, direct injury, ingestion, etc.)
chronic: H. Pylori
What stains are useful for highlighting H. pylori (2)?
- methylene blue stain
- Warthrin-starry stain
Describe the pathogenesis of Autoimmune chronic gastritis and what occurs as a result.
Is the risk of adenocarcinoma affected?
- There are antibodies to parietal cells and IF
- Antrum is spared
- Results in B12 deficiency (IF loss) and resulting anemia
- Also decreased pepsinogen (acid) levels (chief cells loss)
- Increased risk of gastric adenocarcinoma