Leg and Ankle Flashcards
(51 cards)
crural fascia:
- deep fascia of the leg
- gives rise to three septum that divide the leg into four compartments
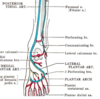
Label:

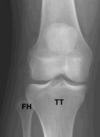
Label:
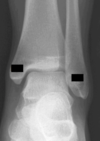

Label:

TibiofibularJoint
What bone of the ankle articulates with the tibia and fibula?
- talus
What bone sits on top of calcaneous?
talus
What bones articulate with talus?
- inferior: calcaneous
- anterior: navicular
Bones in the following compartments:
- hindfoot
- midfoot
- forefoot
- hindfoot: talus and calcaneous
- midfoot: navicular
- forefoot: metatarsals
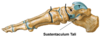
sustentaculum tali:
- shelf part of the calcaneus which supports the talus
- where the spring ligament attaches
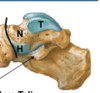
Structure of the talus:
- trochlea: articulates with tibia/fibula
- neck: articulates with sustentaculum tali/calcaneous
- head: articulates with navicularis & sustentaculum tali/calcaneous
What part of the foot allow for twisting motion of the foot?
- midfoot: navicular bone
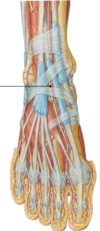
Label:

- CB = cuboid
- LC = lateral cuneiform

Septum of the leg:
- arise from the crural fascia
- anterior intermuscular septum
- posterior intermuscular septum
- transverse intermuscular septum
Borders of the leg compartments:
-
anterior intermuscular septum:
- divides anterior from lateral
-
posterior intermuscular septum:
- divides lateral from posterior superficial
-
transverse intermuscular septum:
- divides poseterior superficial from deep posterior
-
Interosseous membrane:
- divides deep posterior from anterior

Anterior Compartment syndrome:
- When pressure is increased in the anterior leg compartment such that the vascular supply collapses and the superficial fibular nerve is compressed.
- Due to exercise overactivity or trauma.
Symptoms of compartment syndrome:
- pain much more severe than consistent with injury
- burning pain
- leg tightness
Treatment of compartment syndrome:
fasciotomy
Label:


Anterior leg muscles, from lateral to medial:
DHT
- Ext. Digitorum Longus (EDL)
- Ext. Hallucis Longus (EHL)
- Tibialis Anterior (TA)
Point of vulnerability for common fibular nerve:
- head of the fibula - very superficial
- winds around, then goes into the lateral compartment first, and deep fibullar nerve goes to the front

What is this an image of?

Extensor retinacula
- prevent bowstringing of the tendons crossing the ankle joint
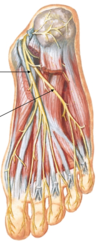
Label:

- nerve: superficial fibular
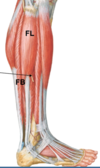
Lateral leg muscles and their function:
- Fibularis Longus (FL)
- Fibularis Brevis (FB)
- Action: ankle eversion
Label:

fibular retinacula