Lower Extremity Muscles Flashcards
(35 cards)

Semimembranosus
Origin: Superior lateral quadrant of the ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Posterior surface of the medial tibial condyle
Action: Extends the thigh, flexes the knee, and also rotates the tibia medially, especially when the knee is flexed
Innervation: Tibial nerve
Arterial Supply: Perforating branches of profunda femoris artery, inferior gluteal artery, and the superior muscular branches of popliteal artery
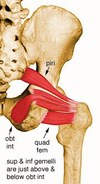
Obturator internus
Origin: Internal surface of obturator membrane and posterior bony margins of obturator foramen
Insertion: Medial surface of greater trochanter of femur, in common with superior and inferior gemelli
Action: Rotates the thigh laterally; also helps abduct the thigh when it is flexed
Innervation: Nerve to the obturator internus and superior gemellus – a branch of the sacral plexus (L5, S1)
Arterial Supply: Internal pudendal and superior and inferior gluteal arteries


Tibialis Anterior
Origin: Lateral condyle of tibia, proximal 1/2 - 2/3 or lateral surface of tibial shaft, interosseous membrane, and the deep surface of the fascia cruris
Insertion: Medial and plantar surfaces of 1st cuneiform and on base of first metatarsal
Action: Dorsiflexor of ankle and invertor of foot
Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
Arterial Supply: Anterior tibial artery
Piriformis
Origin: Anterior surface of lateral process of sacrum and gluteal surface of ilium at the margin of the greater sciatic notch
Insertion: Superior border of greater trochanter
Action: Lateral rotator of the hip joint; also helps abduct the hip if it is flexed
Innervation: Piriformis nerve (L5, S1, S2)
Arterial Supply: Superior and inferior gluteal and internal pudendal arteries

Extensor Digitorum Longus
Origin: Lateral condyle of tibia, upper 2/3 - 3/4 of medial fibular shaft surface, upper part of interosseous membrane, fascia cruris, and anterior intermuscular septum
Insertion: Splits into 4 tendon slips after inferior extensor retinaculum, each of which insert on dorsum of middle and distal phalanges as part of extensor expansion complex
Action: Extend toes 2 - 5 and dorsiflexes ankle
Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
Arterial Supply: Anterior tibial artery

Peroneus Tertius
Origin: Arises with the extensor digitorum longus from the medial fibular shaft surface and the anterior intermuscular septum (between the extensor digitorum longus and the tibialis anterior)
Insertion: Dorsal surface of the base of the fifth metatarsal
Action: Works with the extensor digitorum longus to dorsiflex, evert and abduct the foot
Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve
Arterial Supply: Anterior tibial artery

Peroneus Longus
Origin: Head of fibula, upper 1/2 - 2/3 of lateral fibular shaft surface; also anterior and posterior intermuscular septa of leg
Insertion: Plantar posterolateral aspect of medial cuneiform and lateral side of 1st metatarsal base
Action: Everts foot and plantar flexes ankle; also helps to support the transverse arch of the foot
Innervation: Superficial peroneal nerve (L5, S1, S2); may also receive additional innervation from common or deep peroneal nerves
Arterial Supply: Anterior tibial and peroneal arteries
Inferior Gemellus
Origin: Posterior portions of ischial tuberosity and lateral obturator ring
Insertion: Medial surface of greater trochanter of femur, in common with obturator internus
Action: Rotates the thigh laterally; also helps abduct the flexed thigh
Innervation: Nerve to the quadratus femoris or nerve to the obturator internus or both (L4-S1).
Arterial Supply: Inferior gluteal artery


Adductor Longus
Origin: Anterior surface of body of pubis, just lateral to pubic symphysis
Insertion: Middle third of linea aspera, between the more medial adductor magnus and brevis insertions and the more lateral origin of the vastus medialis
Action: Adducts and flexes the thigh, and helps to laterally rotate the hip joint
Innervation: Anterior division of obturator nerve
Arterial Supply: Obturator artery and medial circumflex femoral artery

Popliteus
Origin: Anterior part of the popliteal groove on lateral surface of lateral femoral condyle
Insertion: Posterior surface of tibia in a fan-like fashion, just superior to the popliteal line
Action: Rotates knee medially and flexes the leg on the thigh
Innervation: Tibial nerve (L4, L5, S1)
Arterial Supply: Medial inferior genicular branch of popliteal artery and muscular branch of posterior tibial artery
Tensor Fascia Latta
Origin: Anterior superior iliac spine, outer lip of anterior iliac crest and fascia lata
Insertion: Iliotibial band
Action: Helps stabilize and steady the hip and knee joints by putting tension on the iliotibial band of fascia
Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
Arterial Supply: Superior gluteal and lateral circumflex femoral artery


Soleus
Origin: Posterior aspect of fibular head, upper 1/4 - 1/3 of posterior surface of fibula, middle 1/3 of medial border of tibial shaft, and from posterior surface of a tendinous arch spanning the two sites of bone origin
Insertion: Eventually unites with the gastrocnemius aponeurosis to form the Achilles tendon, inserting on the middle 1/3 of the posterior calcaneal surface
Action: Powerful plantar flexor of ankle
Innervation: Tibial nerve (S1, S2)
Arterial Supply: Posterior tibial, peroneal, and sural arteries
Gracilis
Origin: Inferior margin of pubic symphysis, inferior ramus of pubis, and adjacent ramus of ischium
Insertion: Medial surface of tibial shaft, just posterior to sartorius
Action: Flexes the knee, adducts the thigh, and helps to medially rotate the tibia on the femur
Innervation: Anterior division of obturator nerve
Arterial Supply: Obturator artery, medial circumflex femoral artery, and muscular branches of profunda femoris artery


Rectus Femoris
Origin: Straight head from anterior inferior iliac spine; reflected head from groove just above acetabulum
Insertion: Base of patella to form the more central portion of the quadriceps femoris tendon
Action: Extends the knee
Innervation: Muscular branches of femoral nerve
Arterial Supply: Lateral circumflex femoral artery

Peroneus Brevis
Origin: Inferior 2/3 of lateral fibular surface; also anterior and posterior intermuscular septa of leg
Insertion: Lateral surface of styloid process of 5th metatarsal base
Action: Everts foot and plantar flexes ankle
Innervation: Superficial peroneal nerve (L5, S1, S2)
Arterial Supply: Muscular branches of peroneal artery

Biceps femoris short head
Origin: Lateral lip of linea aspera, lateral supracondylar ridge of femur, and lateral intermuscular septum of thigh
Insertion: Primarily on fibular head; also on lateral collateral ligament and lateral tibial condyle
Action: Flexes the knee, and also rotates the tibia laterally; long head also extends the hip joint
Innervation: Common peroneal nerve
Arterial Supply: Perforating branches of profunda femoris artery, inferior gluteal artery, and the superior muscular branches of popliteal artery
What muscle

Psoas and iliacus
Origin: Anterior surfaces and lower borders of transverse processes of L1 - L5 and bodies and discs of T12 - L5
Insertion: Lesser trochanter (as ileopsoas)
Action: Flex the torso and thigh with respect to each other
Innervation: Direct fibers of L1 - L3 of lumbar plexus
Arterial Supply: Lumbar branch of iliopsoas branch of internal iliac artery
Quadratus Femoris
Origin: Lateral margin of obturator ring above ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Quadrate tubercle and adjacent bone of intertrochanteric crest of proximal posterior femur
Action: Rotates the hip laterally; also helps adduct the hip
Innervation: Quadratus femoris branch of nerve to the quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus (L5, S1)
Arterial Supply: Medial circumflex femoral artery, inferior gluteal artery, 1st - 4th perforating arteries, obturator artery, and some superior muscular branches of popliteal artery

Pectineus
Origin: Pecten pubis and pectineal surface of the pubis
Insertion: Pectineal line of femur
Action: Adducts the thigh and flexes the hip joint
Innervation: Femoral nerve usually, although it may sometimes receive additional innervation from the obturator nerve as well
Arterial Supply: Medial circumflex femoral branch of femoral artery and obturator artery

Superior Gemellus
Origin: Ischial spine
Insertion: Medial surface of greater trochanter of femur, in common with obturator internus
Action: Rotates the thigh laterally; also helps abduct the flexed thigh
Innervation: Nerve to the obturator internus or nerve to quadratus femoris or both (L4-S1)
Arterial Supply: Inferior gluteal artery

Vastus Muscles
Vastus Intermedius
Origin: Superior 2/3 of anterior and lateral surfaces of femur; also from lateral intermuscular septum of thigh
Insertion: Lateral border of patella; also forms the deep portion of the quadriceps tendon
Action: Extends the knee
Innervation: Muscular branches of femoral nerve
Arterial Supply: Lateral circumflex femoral artery
Vastus Lateralis
Origin: Superior portion of intertrochanteric line, anterior and inferior borders of greater trochanter, superior portion of lateral lip of linea aspera, and lateral portion of gluteal tuberosity of femur
Insertion: Lateral base and border of patella; also forms the lateral patellar retinaculum and lateral side of quadriceps femoris tendon
Action: Extends the knee
Innervation: Muscular branches of femoral nerve
Arterial Supply: Lateral circumflex femoral artery
Vastus Medialis
Origin: Inferior portion of intertrochanteric line, spiral line, medial lip of linea aspera, superior part of medial supracondylar ridge of femur, and medial intermuscular septum
Insertion: Medial base and border of patella; also forms the medial patellar retinaculum and medial side of quadriceps femoris tendon
Action: Extends the knee
Innervation: Muscular branches of femoral nerve
Arterial Supply: Femoral artery, profunda femoris artery, and superior medial genicular branch of popliteal artery

Iliacus
Origin: Upper 2/3 of iliac fossa of ilium, internal lip of iliac crest, lateral aspect of sacrum, ventral sacroiliac ligament, and lower portion of iliolumbar ligament
Insertion: Lesser trochanter
Action: Flex the torso and thigh with respect to each other
Innervation: Muscular branch of femoral nerve
Arterial Supply: Lumbar branch of iliopsoas branch of internal iliac artery


Gluteus Minimus
Origin: Dorsal ilium between inferior and anterior gluteal lines; also from edge of greater sciatic notch
Insertion: Anterior surface of greater trochanter
Action: Abducts and medially rotates the hip joint
Innervation: Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1)
Arterial Supply: Superior gluteal artery
Tom, Dick, and Harry

Tibialis Posterior
Origin: Posterior aspect of interosseous membrane, superior 2/3 of medial posterior surface of fibula, superior aspect of posterior surface of tibia, and from intermuscular septum between muscles of posterior compartment and deep transverse septum
Insertion: Splits into two slips after passing inferior to plantar calcaneonavicular ligament; superficial slip inserts on the tuberosity of the navicular bone and sometimes medial cuneiform; deeper slip divides again into slips inserting on plantar surfaces of metatarsals 2 - 4 and second cuneiform
Action: Principal invertor of foot; also adducts foot, plantar flexes ankle, and helps to supinate the foot
Innervation: Tibial nerve (L4, L5)
Arterial Supply: Muscular branches of sural, peroneal and posterior tibial arteries
Flexor Digitorum Longus
Origin: Posterior surface of tibia distal to popliteal line
Insertion: Splits into four slips after passing through medial intermuscular septum of plantar surface of foot; these slips then insert on plantar surface of bases of 2nd - 5th distal phalanges
Action: Flexes toes 2 - 5; also helps in plantar flexion of ankle
Innervation: Tibial nerve (S2, S3)
Arterial Supply: Muscular branch of posterior tibial artery
Flexor Hallucis Longis
Origin: Inferior 2/3 of posterior surface of fibula, lower part of interosseous membrane
Insertion: Plantar surface of base of distal phalanx of great toe
Action: Flexes great toe, helps to supinate ankle, and is a very weak plantar flexor of ankle
Innervation: Tibial nerve (S2, S3)
Arterial Supply: Muscular branch of peroneal and posterior tibial artery













