Lower limb Flashcards
(139 cards)
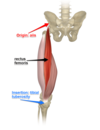
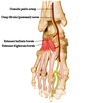
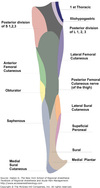
Borders of the femoral triangle
superior - inguinal ligament
lateral - medial border of sartorius
medial - medial border of adductor longus
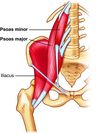
floor - pectineus, iliopsoas and adductor longus
root - fascia lata

Content of femoral triangle
Femoral nerve
Femoral artery
Femoral vein
Femoral lymph nodes/canal

What is the femoral sheath?
Continuation of the fascia lining the abdomen
Anterior wall - continuous with fascia transversalis
Posterior wall - continous with fascia iliaca.
Sheath surrounds the femoral vessels and lymphatics for about 2.5cm below the inguinal ligament.

Content of femoral sheath
Femoral artery, vein and canal

Borders of Femoral canal (femoral ring)
Small medial compartment of the femoral sheath.
At the superior aspect is called the femoral ring:
Roof - inguinal ligament
lateral - femoral vein
medial - lacunar ligament
floor - pectineal ligament

Content of femoral canal
lymph nodes (femoral hernia)
How does a femoral hernia present?
Femoral hernia get hernial sac passing down femoral canal pushing septum (forms opening of femoral ring) before it
When passes out of bottom end of femoral canal forms a swelling in upper part of thigh deep to fascia
Swelling will lie below and lateral to pubic tubercle
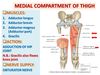
Borders of adductor canal/hunter’s canal
Runs from apex of femoral artery to opening in adductor magnus.
Floor - adductor longus and magnus
Lateral - vastus medialis extends from the apex of femoral triangle to adductor hiatus
Sup: from apex Fem triangle
Inferiorly - adductor hiatus in adductor magnus
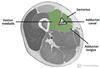
Content of adductor canal / hunter’s canal
Femoral artery
Femoral vein
Saphenous nerve
Terminal part of obturator nerve

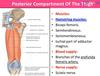
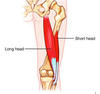
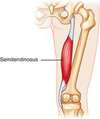
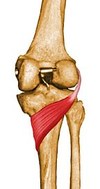
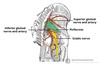
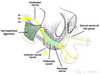
Borders of Popliteal fossa
Inferior - 2 heads of gastrocnemius and plantaris
Lateral - biceps femoris
Medial - semimembranosus floor - posterior joint capsule
Roof - popliteal fascia

Content of popliteal fossa
popliteal artery
popliteal vein
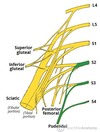
tibial nerve
common peroneal nerve
Popliteal lymph nodes

What is the relationship of structures at the popliteal fossa?
Tibial and common fibular nerves (follows biceps femoris tendon) - superficial
Small saphenous vein
Deepest structure is the popliteal artery
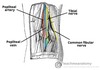
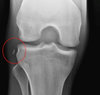
Hip joint
Ball and socket joint, articular cartilage
Acetabulum (pubis, ischium, ilium) and femoral head
3 ligaments:
- *Pubofemoral** (superior pubic rami to intertrochanteric line)
- *Ischiofemoral** (ischium to greater trochanter) - weaker point
- *Iliofemoral** (AIIS to intertrochanteric line) - strongest point ligament of head of femur (contains a branch of obturator artery)
medial circumflex femoral artery (branch of profunda femoris) supplies the femoral head
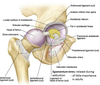
What does the sacrotuberous ligament connect?
Connects the back of the sacrum to the ischial tuberosity

What does the sacrospinous ligament connect?
Connects back of sacrum to spine of ischium

Hip muscles - superficial abductors and extensors
Gluteus maximus
Gluteus medius
Gluteus minimus
Tensor Fascia Lata

Gluteus maximus
origin - posterior surface of Ilium, sacrum, coccyx
insertion - Gluteal tuberosity of the femur, fascia lata
innervation - inferior gluteal nerve action

Gluteus medius
origin - iliac crest
insertion - lateral surface greater trochanter of femur
innervation - superior gluteal nerve
action - abductor, internal rotation
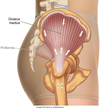
gluteus minimus
Origin- ilium
insertion - anterior greater trochanter of femur
innervation - superior gluteal nerve action - abductor hip, internal rotation
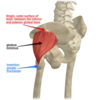
Tensor fascia lata
origin - anterior iliac crest, ASIS
insertion - iliotibial band ( which extends to popliteal fascia, lateral condyle of tibia)
innervation - femoral nerve
action - abductor and internal rotation
Role in tensing FASCIA LATA

Attachment of fascia lata
Posterior - sacrum and coccyx
Lateral - iliac crest
Anterior - inguinal ligament, superior pubic rami
Medial - Ischiopubic rami, ischial tuberosity , sacrotuberous ligament
Distally - lateral tibial condyle
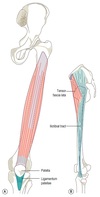
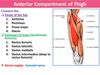
What is the role of the fascia lata in the leg?
Gives rise to three intermuscular septa that attach centrally to the femur.
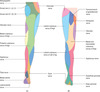
The septa divide the thigh musculature into three compartments;
anterior
medial
lateral
The lateral intermuscular septum is the strongest of the three due to reinforcement from the iliotibial tract

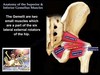
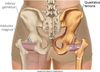
Hip muscles - deep lateral rotators
Piriformis
Gemelli
Obturator internus
Quadratus femoris
Piriformis
origin - anterior surface of sacrum
insertion - greater trochanter of femur
innervation - nerve to piriformis
action - lateral rotation, abduction passes through the GREATER sciatic foramen