LS-3 ASM Flashcards
(33 cards)
Create a simple program that loads data into register one, perform a bit-wise not operation and store that in result.
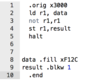
Each non blank line in lc-3 is what?
- An instruction (ld r1, data)
- An assembler directive (.orig x3000)
- A comment
What is the typical form an instruction has in LC-3?
Label OpCode Operands ;Comments
What does an instruction consis of?
An opcode and one or more operands
What are opcodes?

What does Operands do? And what are typical operands?

Line by line, what does the following code do?


How would you load data into register 1?
ld R1, data
How do you store the contents of register 3 into result?
st R3, result
What can you think of labels as?
They are a symbolis name for a memory location (the line is usually denoted by a hex value)
How do Assembler Directives work?
What are the Assembler Directives/What do they do

In general what are traps?

What are the traps and what do they do?

In general how does the Assembly process work?

What happens during the first pass of the assembly process

What happens during the second pass of the assembly process
Each line scanned again
Everything translated into machine languge
Does using the symbol tables, fillng in labels like a macro.
Fill memory loctions as directed by assembly directives
In general what is Linking and Loading?

What are the output files the Assembler generates?

How do you read in a character and how do you print that character to console?

How do you print a string to console?

In general, what is a condition code?
There is a process to determine based on the last arithmatic/logic expression if the result was zero, poisitive or negative.
What are the instructions that affect the condition code?

What is the condition code after each line of code?


How does conditional branching work?










