Lung Exam 101 Flashcards
(42 cards)
What is the traditional order of the pulmonary exam?
- inspection 2. palpation 3. percussion 4 auscultation
What are some things to look for upon inspection?
- General appearance [do they look sick or well?] 2. Is the breathing comfortable or labored? 3. Do you hear any audible breath sounds? 4. How is their coloring? 5. Clubbing of digits? 6. Signs of chronic corticosteroid use [thinning or bruising of skin; redistribution of fat to their trunks and face?
What is Cushing’s syndrome?
When someone has abnormally high levels of cortisol. The most common reason why this happens is from overuse of corticosteroid medications. Excess corticosteroids are frequently given for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
What is a cardinal sign of pulmonary disease?
clubbing of the digits
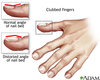
What are the diagnostic criteria for clubbing?
- increased interphalangeal depth ratio [end segment of finger is thicker when viewed in profile than the middle segment].
- increased hyponychial [Lovibond] angle, the angle from the finger to the nail [normally about 160 degrees when seen in profile]
- Postive Schamroth sign - obliteration of space between fingers when the nails are placed face to face - the normal finding is a diamond of light coming through because the preserved angle is less than 180 degrees
- when palpating the clubbed digits, the increased connective tissue is spongy, and the nail can be easily rocked back and forth by putting alternating pressure on the proximal and distal edges of the nail as if the nail were a see-saw
Define Kussmaul’s respirations
regular, rapid, and deep respirations seen in patients with metabolic acidosis [both hyperpnea and tachypnea]
Define Cheyne-Stokes respirations
characterized by periods of increasing hyperpnea that peak, then slow to an apeneic period, followed by resumption of breathing and hyperpnea
This is seen in severe congestive heart failure and stroke, seen especially when the patient is sleeping
What can pursed-lip breathing indicate?
obstructive lung disease [such as emphysema]
What does the use of accessory muscles during breathing indicate?
This is a sign of respiratory difficulty
What accessory muscles are involved in inhalation?
sternocleidomastoid, scalene, and intercostal muscles
What accessory muscles are involved in exhalation?
abdominal muscles
Define respiratory paradox.
This is when the abdomen retracts [moves inward] during inspiration when it should expand outward during inspiration.
This is seen in patients with weaknes or paralysis of the diaphragm.
What may a trachea deviated to one side indicate?
May be devaited towards a collapsed lung or away from a pneumothorax [air in the pleural cavity under high pressure], a large pleural effusion, or pneumonia.
Describe where the different lobes project on the chest.
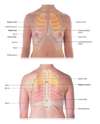
Define tactile fremitus
the palpable vibrations felt on the chest when patients speak
What may a decreasd fremitus mean?
May be dut to fluid, air, or a mass
What may an increased fremitus mean?
Felt in pneumonia [sound waves travel better through consolidated lung than air-filled lung]
Describe tactile fremitus for lower pitched sounds and higher pitched sounds
lower pitched sounds: more fremitus
higher pitched sounds: fainter fremitus
Describe the common sounds heard when percussing areas of the body.
- Flat: the tone/sensation felt when you precuss the thigh
- Dull: found wehn percussing over the liver [or over a pleural effusion, a collection of fluid in the pleural space]
- Resonant: found over normal lung
- Hyperresonant: found over emphysematous lungs
- Tympanitic: found over a pneumothorax [similar to the thone over the gastric air bubble]
What are the two basic lung sounds when air moves in and out of the airways?
- vesicular [normal] breath sounds
- bronchial [tubular] breath sounds
Define vesicular breath sounds
- heard over normal, health lungs
- inspiratory phase is louder and longer [about 3:1] than the expiratory phase
- no gap between the two phases
Define bronchial breath sounds
- loud in both inhalation and exhalation
- sound like Darth Vader breathing [tubular quality]
- may have a gap between the two phases
- bronchial breath sounds are heard over areas of lung that are fluid filled [as in pneumonia] or collapsed, as in compressed lung tissue above a pleural effusion
- bronchial breath sounds may also be heard over parasternal and parascaupular areas in healthy patients
Define parasternal area.
k.
Define parascapular area.
k


