Lungs Flashcards
(11 cards)
What are the features of the lungs: a.k.a surfaces and borders?
- Base-sits on diaphragm
- Apex (~highest part)-extends above rib I and to the neck
- 2 surfaces- costal surface associated with the ribs and ICS. Mediastinal surface.
- 3 borders- separate the surfaces. Inferior border- separate the costal surface and base. Anterior and posterior border-separate the costal and mediastinal surface.

Describe the root and hilum of the lung and what it contains? What is the function of the pulmonary ligament?
The root of the lung contains collection of structures (pulmonary artery/vein and bronchi) which is contained in a sleeve of mediastinal pleura. The root joins the medial surface of the lung called the hilum where structures leave and enter. (hilum~notch where BV/nerves enter and leave) The sleeve of mediastinal pleura projects inferiorly to form the pulmonary ligament (blade-like) that extends from the hilum to the mediastinum. It has two functions: • Secure the inferior lobe of the lung • Accommodate the structures from moving up and down during inspiration/expiration

What are the nerves that run in front/behind the hilum of lung?
• Phrenic nerve-runs in front of root of lung • Vagus nerves- runs behind root hilum of lung
Describe the features of the right lung and its associated structures on the mediastinal surface?
The right lung, unlike the left contains 3 lobes: superior, middle and inferior lobe. These are separated by 2 fissures: • Horizontal fissure-separating the superior and middle lobe. Meets oblique fissure at rib V and then runs the course along 4th ICS. • Oblique fissure-separates the middle and inferior lobe. Starts roughly at spinous process of T4, crosses 5th ICS and runs course along rib VI. Structures on mediastinal surface: • Heart • Superior vena cava (SVC) • Inferior vena cava (IVC) • Azygos vein (drains into SVC) • Oesophagus behind

Describe features of left lung and its associated structures on mediastinal surface?
The left lung, unlike the right, consists of 2 lobes: superior and inferior. These are separated by 1 fissure: • Oblique fissure-runs slightly more oblique in left; starts at spinous process of T3/T4, runs across 5th ICS and along contour of rib VI. The superior lobe of the left lung has a cardiac notch where the heart is, and inferior to that there is a lingula (latin~for little tongue) just beneath the notch. Structures on mediastinal surface: • Heart • Aortic arch and thoracic aorta • Oesophagus behind

What are the features of bronchial tree?
• Trachea- from CVI to TIV, divides into the right and left main bronchus at the carina (last cartilage ring).
The trachea is supported anteriorly by c-shaped cartilage rings that prevent it from collapsing during inspiration, posteriorly by smooth muscle.
- Right and left main bronchus enter the root and the hilum of the lung, where it divides into the lobar bronchi
- Lobar bronchi supply each lobe of the lung, before dividing into the segmental bronchi
- Segmental bronchi supply each bronchopulmonary segment, and divides several times before ending with terminal bronchiole.
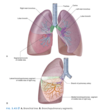
What are the 10 bronchopulmonary segments on each lung?
Right bronchopulmonary segment: • Superior lobe-apical, anterior, posterior segments • Middle lobe-medial, lateral segments • Inferior lobe- superior segment; anterior, lateral and posterior basal segment. Middle basal segment only seen in mediastinal surface Left bronchopulmonary segment: • Superior lobe-apical, anterior and posterior segments; superior and inferior lingular segments • Inferior lobe- superior segment; anterior, lateral and posterior basal segment. Middle basal segment can be seen on mediastinal surface.

Describe the arterial supply of the lung/venous drainage
The lung has a right and left pulmonary artery to supply the right and left lungs respectively. The pulmonary arteries bifurcate from the pulmonary trunk, at vertebral level TIV, anteroinferiorly to bifurcation of trachea. • Right pulmonary artery -is longer than left and runs horizontally across mediastinum -anteroinferior to the trachea bifurcation and directly anterior to the right main bronchus -posterior to SVC, ascending aorta and the right superior pulmonary vein • Left pulmonary artery -anterior to the descending thoracic aorta -posterior to left superior pulmonary vein Venous drainage: -superior and inferior pulmonary vein

Describe the lungs own supply of its own parenchyma
• Bronchial artery -bring O2/nutrients to lung tissue -1 right bronchial artery from 3rd posterior intercostal artery -2 left bronchial artery from the thoracic aorta; one superior and one inferior left bronchial artery. • Bronchial veins -bring deoxygenated blood and waste from lung tissue and drain into pulmonary veins/left atrium
Describe innervation of lung and what do the PNS/SNS do respectively?
• Anterior pulmonary plexus-anterior to the trachea bifurcation • Posterior pulmonary plexus-posterior to trachea bifurcation These ultimately stem from the autonomic nervous system: PNS (vagus nerve specifically) and SNS, which give rise to different functions. • Vagus nerve-bronchoconstriction • SNS-bronchodilation
Describe lymphatic innervation of lung
The lungs are drained by the tracheobronchial lymph nodes, at the junction between trachea and main bronchi. These tracheobronchial lymph nodes join with parasternal and brachiocephalic nodes to form the: • Right bronchomediastinal node-drains into the right lymphatic duct • Left bronchomediastinal node-drains into the thoracic duct



