MBB Pathology/Imaging Flashcards
(79 cards)
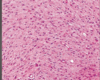
Describe what you see here; what condition is this

rounded atrophic fibers and lymphocytic infiltrate; top right is macrophages attacking muscle fiber; polymyositis
describe the constellation of findings seen and for what disease

a) balooning neuron
b and c) neurofibrillary tau tangles
d) astrocytic plaques
corticobasal degeneration
Describe the difference between hemorrhagic infarct and a intraparenchymal hemorrhage and how they would look micro/macroscopically
Hemorrhagic infarct has brain tissue with blood infiltrating, tissue is becoming necrotic, wil lsee petechiae and neutrophils etc.
intraparenchymal hemorrhage is when blood spills out and pushes brain tissue out of the way and takes up space, so microscopically you would only see blood and fibrin

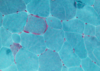
what is this

medulloblastoma
What is going on here, what is causing it

central herniation of temporal lobes, brainstem bein displaced downward, severing basilar pontine arteries, fatal (overall cause is edema)
What is going on in this image? what condition is this common in

asymmetrical atrophy; corticobasil degeneration
What is this? What conditions is this common in

lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease, Lewy body dementia
What is this, what is the most common cause, is it fast or slow growing

subdural hemorrhage, trauma, slow growing
describe what you see; what condition is this common in

ballooned neuron; corticobasil degeneration
Name 3 possible causes of this

high grade glioma (GBM)
cns lymphoma
rlly bad MS
describe what you see; what type of cancer is this; what age group is involved

dense eosinophilic rosenthal fibers; pilocytic astrocytoma children
Describe the process going on here from left to right and what kind of process is this?

myopathic process
1) left most: muscle fiber necrosis
2) middle: attempts at regeneration
3) fibrosis
What is going on here; what condition would this be seen in

alpha synnuclein cytoplasmic inclusions in GLIAL cells; multiple system atrophy
What are yo ustaining for here; what disease is this common in

staining for ubiquitin/huntington protein inclusions ; huntington disese
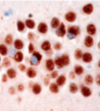
describe what you see; what disease is this

neuronal loss, reactive (alzheimers type 2 ) astrocytes; metabolic gliosis (thing in the center) –> wilson’s disease
what cancer is this
what demographic is it common in

medulloblastoma children
describe the symptoms; what syndrome do they belong to

plexiform neurofibroma on peripheral nervous sytem
cafe au lait spot
neurofibromatosis 1
What is this? Name some causes?

interparenchymal hemorrhage, htn most common, also arteriovenous malformation, lesion, amyloid
describe the two images; what condition is this

swollen neuron aka pick cell
status spongiosis aka vacuolization of the cortex
pick’s disease
what is this, where does it come off of

vestibular schwannoma/acoustic neuroma; nerve VIII at the cerebellopontine angle
describe what yo usee; what cancer is this

vascular tumor, vacuolated stroma, hemangioblastoma from von hippel lindau
Describe these findings; what condition is this associated with

different manifestations of tau protein accumulations
left is neurfibrillatory tangles
bottom left is tufted astrocytes
right (c shpaed) is glial inclusions (also neuronal inclusions)
PROGRESSIVE SUPRANUCLEAR PALSY
Describe what is happening here: what condition is this

perifascicular atrophy; dermatomyositis
describe each of the three images; what disease is this
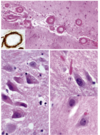
top- cerebral amyloid angiopathy (amyloid depositing in leptomeningeal and intraparenchymal arteries)
bottom left- granulovaculoar degeneration (clear cytoplasmic inclusions with basophilic granules)
bottom right- hirano bodies, glassy eosinophilic bodies made of actin
alzheimers