MEAT INSPECTION Flashcards
(66 cards)

Acute pericarditis

Chronic pericarditis

Gangrenous pericarditis (complication of traumatic reticuloperitonitis)
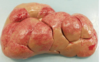
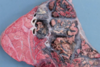
Vegetative valvular endocarditis
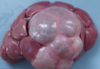
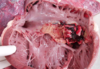
Multiple liver abscesses
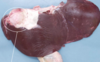
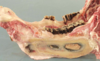
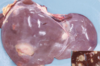
Single liver abscess
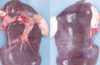
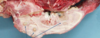
Fasciolosis (mild)
- rounded liver due to enlarged dorsal lobes and atrophied ventral/caudal lobes
- prominent bile ducts

Fasciolosis (moderate)
- rounded liver (enlarged dorsal lobes and atrophied caudal/ventral lobes)
- prominent thickened calcified bile duct
- scarring
Which parasite causes fasciolosis?
Fasciola hepatica

Fasciolosis (severe)
- rounded enlarged liver
- prominent distorted bile duct
- severe scarring
- fluke in bile duct if not adequate immune response
What is the difference between cirrhosis and hepatic fibrosis?
CIRRHOSIS: small, multinodular liver. Fibrosis with regeneration. Rare.
HEPATIC FIBROSIS: uniformly firm. No change in outline. Diffuse fibrosis with NO regeneration. eg. ragwort poisoning

Hydatidosis
What is the cause of hydatidosis?
Intermediate stage of Echinococcus granulosa (dog tapeworm)
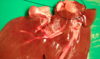
Cysticercus tenuicollis

Cysticercus tenuicollis (parasitic nodules)

Hepatic lipidosis
- friable
- yellow/orange
- swollen
- smell of ketones?

Telangiectasis

Nutmeg liver
-from right sided heart failure-> chronic liver congestion, centrilobular necrosis and fibrosis

Tension lipidosis

Johnes disease
What causes Johne’s disease?
Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis

Generalised peritonitis

Interstitial nephritis
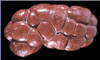
Interstitial nephritis (white spot- acute)