Mechanisms & Causes of Cell Injury Flashcards
(9 cards)
What is autolysis?
Self digestion due to endogenous enzymes
What is bile imbibition?
Postmortem leakage of bile from the gallbladder
Normal Cells
Homeostasis steady state is determined by:
- State of metabolism, differentiation, and specialization
- Constraints of neighboring cells
- Availability to metabolic substrates
- Have the ability to adapt to changes in physiologic states
New steady states achieved→ cell survival → continued function
4 Adaptive Responses
Hypertrophy
- Increase in cell size
Hyperplasia
- Increase in cell number
Atrophy
- Decrease in cell size and metabolic activity
Metaplasia
- Change in cell phenotype
- Ex. tracheal columnar epithelial cell changes to a squamous epithelial cell
Elimination of added stress = cell returns to normal state without negative consequences
What is cell injury?
Something that disrupts cellular homeostasis
- Injury if limits of adaptive responses are exceeded
- Injury if exposed to injurious agents
- Injury if deprived of required nutrients
- Injury via mutations that affect cellular constituents
- Ex. Neoplasia, Heritable diseases
Consequences of Cell Injury:
2 Options
2 options:
- Reversible injury
- Functional & morphologic changes that occur with injury are reversible up to a certain point
- The cell can “restore” itself/return back to homeostasis
- Damage from stimulus can be fixed
- Irreversible Injury
- If stimulus persits or is severe enough from start →
- Cell suffers irreversible cell injury →
- Cell death
Line between reversible & irreversible is blurry
Causes & Mechanisms of Cell Injury
Causes:
- Numerous & diverse
- Intrinsic & extrinsic
All causes activate 1+ of four common final mechanisms that lead to cell injury:
- ATP depletion
- Permeabilization of the cell membrane
- Disruption of biochemical pathways
- Damage to DNA
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: ATP Depletion
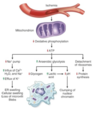
ATP required for all anabolic/catabolic processes within cell:
- Membrane transport
- Protein synthesis
- Lipogenesis
- Reactions for phospholipid turnover
Under ischemic conditions (low O2), what effect does ATP depletion have on the cell?

Under ischemic conditions (Low O2):
Decreased function of Na+/K+ ATPase→
- Increased intracellular Ca2+ = damage to cell
- Increased intracellular Na+ = influx of H2O
- Increased loss of K+ from cell
All lead to cell swelling


