Memory List Flashcards
(44 cards)
Kinematics
The study of the mathematics of motion without regard to the forces involved.
Kinetics
The study of the force-motion relationship.
Particle Dynamics
An object whose motion may be analyzed without regard to rotation about an axis through the object.
Rigid Body
An object whose motion may not be analyzed without regard to rotation about an axis through the object.
Position Vector
A vector whose tip indicates the location of a point (particle) or a point on a rigid body.
Velocity Equation

Acceleration Equation

V-DOT-S-V Equation
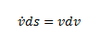
Cartesian Coordinates
Rectangular Coordinates
Vector
A vector has magnitude and direction.
Position Vector in Cylindrical Coordinates

Velocity Vector in Cylindrical Coordinates
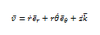
Acceleration Vector in Cylindrical Coordinates

Particle
An object whose motion may be analyzed without regard to rotation about an axis through an object.
Clues to use Rectangular Coordinates
- Rectilinear Motion
- Simple Projectile Motion
- Acceleration in a given direction that depends only on time and/or motion parameters in that direction.
Velocity in Normal & Tangental Coordinates

Acceleration in Normal & Tangental Coordinates

Path
Locations of the tips of the r-bars.
Relative Position
(Position of B with respect to A)

Newton’s 1st Law
An object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force. An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force.
Newton’s 2nd Law

Newton’s 3rd Law
The forces of action and reaction are equal in magnitude, but opposite in sign.
Inertial Reference Frame
Fixed reference frame.
Inertia
Resistance to acceleration.