MHD Flashcards
(117 cards)
What is the relationship between Calveolin and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Epithelial activation/injury leads to the release of TGF-B1 and this goes to block Caveolin in the fibroblasts. Caveolin normally functions to block deposition of collagen and extracellular matrix. W/o Caveolin, pulmonary fibrosis has a clearer path to development.
Anthracosis
Deposition of coal dust in the lungs
One form of Pneumoconioses (other examples include silicosis and asbestosis)
What is the key characteristic of sarcoidosis?
Non-caseating granulomas
What are Schaumann bodies and Asteroid Bodies, and what disease process are they associated with?
Schaumann: Concretions (hard masses) of calcium and protein
Asteroid: Star like stellate inclusions
Both found in SARCOIDOSIS
What changes in FEV1 w/ a bronchodilator defines reversibility?
12% and 200cc’s
99% of obstructions are _________ (upper/lower) airway.
Lower
Equation for Diffusion Capacity
DLCO = [CO]inhaled - [CO]exhaled
This is the difference between the CO inhaled and the CO exhaled, which tells you how much ended up diffusing into the blood.
If DLCO is low, but spirometry and lung volumes are normal, what lung issue might you suspect?
Pulmonary HTN
What are the (3) main components to a PFT and what do they each tell you?
- Spirometry (used to ID obstruction)
- Long Volume Determination (used to ID restriction)
- Diffusion Capcity Measurement (used to ID diffusion defect)
What are the (4) Categories for Asthma and what values define each (based on each criteria below):
*daytime symptoms/wk, nighttime symptoms/mo, FEV1 or PEFR, PEFR variability

RADS
Reactive Airway Dysfunction Syndrome
No prior asthma, then a “big-bang” exposure (ex. 9/11) leads to asthma which normally resolves in 6 months or so.
Samter’s Triad
A triad of symptoms which point to aspirin sensitivity:
- Asthma
- Nasal polyposis
- NSAID sensitivity
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillous
Asthma + Allergic response (+ skin test, IgE, eosinophils, etc.)
Stages of Sarcoidosis based on CXR
LAD = lymphadenopathy
ILD = Interstitial lung disease

What are your (3) main differentials when a pt presents w/ a cough?
- Postnasal drip
- Acid reflux
- Asthma
Fleischner Guidlines
What is it used for, and what are the guidlines?
Used for determining course of action after nodules found on low dose CT scan.

Identify the type of lung cancers being shown in each section
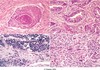
- Squamous cell
- Adenocarcinoma
- Small cell carcinoma
- Large cell undifferentiated carcinoma
Which bug is the most common cause for Community Acquired Pneumonia?
What are the clinical presentations associated with this bug (5)?
What does this bug look like?
Strep Pneumo
Acute onset fever, shaking chill, rusty sputum, shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain
Lancet shaped diplococcus
ALL
Name the cytogenic markers which correlate with a good prognosis.
Name the cytogenic markers which correlate with a poor prognosis.
Good sign:
- t(12;21) [TEL1-AML1]
- Hyperdiploidy
Poor signs:
- t(9;22) [BCR-ABL] - Philidelphia chromosome
- t(4;11) [AF4-MLL]
Name the 4 WHO classifications of AML
What are the affliated cytogenic markers and what do they indicate?
- AML w/ recurrent genetic abnormalities
- t(15;17)PML/RARA good prognosis
- t(11q23;v)MLL poor prognosis
- AML arising from Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) poor prognosis
- Therapy Related poor prognosis
- post chemo/radiation
- NOS intermediate prognosis
What is Myelodysplastic syndrome? What can it progress to?
It is also known as “preleukemia”
Hypercellular bone marrow which leads to a peripheral cytopenia and many morphological abnormalities. Often progresses to AML.
Poor prognosis
Acute Promyelocytic Anemia
What is it a type of? What is the genetic change? What does it increase risk of? How is it treated? What is the prognosis?
It is one of the classifications of AML
t(15;17)PML/RARA
There is fusion between the PML/Retinoic Acid Receptor genes creating an abnormal RAR.
Greatly increased risk of DIC due to the presence of MPO based auer rods.
Great prognosis if treated with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)
What is SIRS and what qualifications must be present for something to count as SIRS? (4 total options)
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome
Massive inflammatory reaction from systemic cytokine release
At least 2 of the following must be present:
- Temperature >38° C or
- Heart rate >90
- Respiratory rate >20 or PaCO2
- WBC >12,000 or 10% immature
What are the (2) key cytokines in Sepsis Syndrome?
What 3rd cytokine has a key role?
TNFa and IL-1
IL-6 also plays a key role


