Micro Images Flashcards
(42 cards)
A patient complaining of discharge has this appearance on pelvic exam. How do you treat?

Metronidazole for pt AND PARTNER
(Frothy yellow discharge = trich = protozoa = metronidazole)
Tx?

Cephalosporin + azithro or doxy to cover Chlamydia
(Ox + = GC)
List at least two tests you would run on a patient with this finding.

US/CT/MRI looking for aortic aneurysm
Neurological tests
(This is a gumma of tertiary syphilis for which aortic aneurysms and dementia are common manifestations; serological testing is not very useful in this late stage)
Complication of this condition?

Respiratory distress, causing a 3% mortality rate per year in patients with infantile laryngeal papillomas due to HPV
Causative agent?

Chlamydia trachomatis L1-L3
(LGV)
Pt presents with headache and fever. Culture of CSF reveals this finding. Dx?

HSV meningitis
(Cytopathic effect = HSV; presentation + ability to culture from CSF = meningitis; CSF culture usually negative if HSV encephalitis)
Cytology of this lesion would reveal:

Multinucleated giant cells with inclusions
(Tzank cells; multiple vesicles on a red base = HSV)

“Ouch, it hurts”.
Dx?

Chancroid
(H. ducreyi)
This finding is unlikely in which stage of the disease caused by this organism?

Tertiary syphilis
(Dark field microscopy = T. pallidum; few spirochetes can be detected in lesions of tertiary syphilis)
“It burns when I urinate.” Dx?

Ct urethritis
(Milky D/C + dysuria = Ct)
A patient complaining of discharge has this finding on pelvic exam. What is the most appropriate diagnostic test?

Wet mount to look for trich
(Colpitis macularis = “strawberry cervix”; think trich!!)
Which stage of life cycle is the organism in this image in?

Latency
(Koilocytes = HPV infected epithelial cells, which are non-permissive cells where HPV lies latent)
How would you make a definitive diagnosis of the suspected organism?
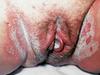
KOH prep
(Vulvovaginal Candidiasis = budding yeast causing white discharge + diaper-rash appearance)
What caused this?
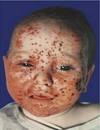
Congenital HSV
(This is eczema herpeticum)
What physical exam finding is unique among STDs to this disease?

Vulvar fissuring
(Caused by edematous response to Candida)
Microscopic examination of this patient’s discharge would likely reveal:

Clue cells
Gram - rods (Gardnerella)
(White, adherent discharge coating the cervix = BV)

Which cell type causes the lesion found here?
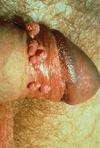
Keratinocytes
(HPV replicates in keratinocytes = permissive cells; latent in germinal cells = non-permissive cells)
What would the causative agent of these lesions look like on gram stain?

Wouldn’t see it on gram stain
(Keratitis [inflammation of cornea] caused by congenital syphilis or HSV 1; T. pallidum too thin for gram stain = must use dark field microscopy; obviously HSV doesn’t gram stain)
Dx?

Hutchison teeth due to congenital syphilis
Your gynecology attending calls you into a room during a colposcopy to ask what you think of this finding. You say….

When treated with acetic acid and viewed with a colposcope, dysplastic cells become white, so this is likely cervical dysplasia, 90% of which is caused by HPV!
A patient complains of a rash on his back and arms. PMH is non-contributory except he mentions he had a small “sore” on his penis a few months ago that didn’t bother him and went away fairly quickly. You decide to biopsy one of the lesions on his back to confirm your suspicion. What do you expect to see on gram stain?
Nothing!
(Syphilis does not gram stain; instead you would do dark field microscopy like the image)
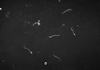
How would you treat this?

Removal
Dx?

Chlamydia trachomatis
(Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies [vacuoles containing bugs] = Ct)
This is a possible complication of which STD? How would the patient present?

Chlamydial cervicitis/urethritis (or LGV?)
Repetitive staccato cough, peripheral eosinophilia, no fever or wheezing
(Infantile pneumonia; notice bilateral infiltrates + hyperinflation)




















