Microbiology Flashcards
(61 cards)
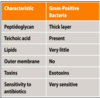
Microbiology
Structure of a bacterial cell

Microbiology
What the bacterial cell wall does
Resists environmental stress like osmatic pressure
Acts as a barrier
Provides mechanical strength
Microbiology
Gram positive cell wall structure

Microbiology
Gram negative cell wall structure


Coccus

Bacillus

Vibrio

Spirochete


Microbiology
Which type of bacteria retain the purple dye in the gram stain test?
Gram positive
Microbiology
Polymers that may also be present in the cell walls of gram positive bacteria
Teichic acids
M protein
Mycolic acid
Microbiology
Teichoic acid
May appear in cell walls of gram positive bacteria
Provides rigidity to the cell wall
Microbiology
M protein
May be found in the cell wall of gram positive bacteria
Helps to prevent phagocytosis by immune cells
Microbiology
Mycolic acid
May be found in the cell wall of gram positive bacteria
Waxy lipid
Aids survival in environmental stress
Provides a barrier to antibiotics
Microbiology
Virulence factor that provides a barrier to antibiotics
Mycolic acid
Microbiology
Catalase test
Tests for enzyme catalase
Microbiology
Catalase
Enzyme required by many organisms for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen
Microbiology
Gram negative bacteria unique outer membrane of the cell wall is called?
Lipopolysaccharide layer (LPS)
Microbiology
What’s unique about the LPS layer?
It is made up of lipopolysaccharides instead of the standard phospholipid molecules
Microbiology
What are the 2 parts of the LPS layer and their roles?
Lipid A
- Anchors the LPS to the phospolipid bilayer
O polysaccharides
- Carbohydrate chains facing the extracellular fluid
Microbiology
Role of the LPS layer
Acts as a major barrier to the outside world
Offers protection against antiseptics and antibiotics
Acts as an endotoxin
Microbiology
How is an endotoxin released?
When the cell lyses and dies
Microbiology
What is the cause of most symptoms of gram negative bacteria
The LPS which acts as an endotoxin