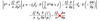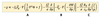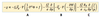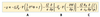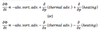mid term MEMORIZING Flashcards
(42 cards)
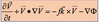
vector form of horizontal momentum equation in (x,y,p) coordinate system
Thus the forcing of the ageostrophic wind can be divided conveniently into the two parts,
the isallobaric wind and the advective wind.
geopotential tendancy
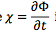
From the above (15) it follows that the isallobaric wind is determined by
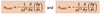
the gradient of the isolines of do p/do t
the isallobaric wind is determined by the gradient of the isolines of do p/ do t
these are
the lines connecting the equal amounts of surface pressure change (isallobars)
at point a
at point b

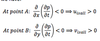
The direction of the isallobaric wind is perpendicular to
the isallobars
The direction of the isallobaric wind is perpendicular to the isallobars, always pointing towards the
falling pressure
The direction of the isallobaric wind is perpendicular to the isallobars, always pointing towards the falling pressure (i.e., pointing to the
minimum value where the strongest pressure decrease) in surface pressure is located.
the advective wind arises when the
geostrophic wind is not uniform, as in diffluent or confluent flow pattern.
In diffluent flow pattern (fig), the geostrophic wind decreases
in positive x-direction
in diffluent flow pattern (fig), the geostrophic wind decreases in positive x-direction due to
the larger spacing between the isobars indicating smaller pressure gradient.
as u > 0
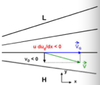
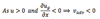
in this case the wind speed will
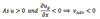
decrease
In the analogous case of a confluent flow the wind speed will
increase
When heights are falling the isobaric wind is
convergent

when hights are rising the isallobaric wind is
divergent
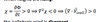
When there is Positive Vorticity Advection (PVA) the advective wind is
divergent
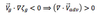
When there is Negative Vorticity Advection (NVA) the advective wind is
convergent
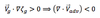
static stability parameter
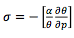
static stability parameter is a positive number for a
stable atmosphere
the equation states that
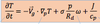
temperature change at a particular location and height is a function of temperature advection by geostrophic wind and vertical motion.
temperature advection relationship
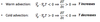
vertical motion relationship