Midterm 3 Flashcards
(117 cards)
What are the 3 general steps for cell signaling?
- Reception - Ligand (primary messenger) binds to receptor
- Transduction - Via secondary messengers
- Response - Cellular responses

What are the 5 features of signal transducing systems?
- Specificity - ligand specific for receptor
- Amplification - Enzymes amplify enzymes, signal increased exponentially
- Modularity - Chemical modifications (phosphorylation)
- Desensitization/Adaptation - Feedback circuit to shutdown signal
- Integration - When 2 signals have opposite effect, net effect will occur

Hormones can be categorized into what 3 categories?
- Endocrine - distant target cell (e.g. insulin)
- Autocrine - self target (e.g. growth factor)
- Paracrine - nearby target cell (e.g. neurotransmitters)
Amino acid derived hormones are derived from which amino acid? What are 2 examples?
Tyrosine
e.g. epinephrine, dopamine
What are peptide hormones? What are 2 examples?
Hormones consisting of 2-100 amino acids.
e.g. Insulin, glucagon
Which hormones can and cannot enter the cell via diffusion?
`AA derived - CANNOT enter cell so binds to receptor
Peptide - CANNOT enter cell so binds to receptor
Steroid - CAN diffuse through hydrophobic membrane
Steroid hormones are derived from __________.
cholesterol
Where do steroid hormones bind and what is the response?
Bind to nuclear receptors inside cytoplasm that regulate transcription factors and control gene expression
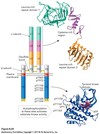
What are the 5 classes of receptor proteins in eukaryotes?
- G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR)
- Receptor tyrosine kinases
- Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)
- Nuclear receptors
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine receptor
What are nicotinic acetylcholine receptors?
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are ligand-gated ion channels.
- Acetylcholine binds to the α subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.
- Ion channel opens and allows Na+ and K+ ions to flow across the membrane and depolarize the cell.

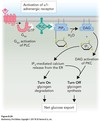
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) is a ________ messenger that is activated by _________ __________.
secondary
adenylate cyclase
ATP + adenylate cyclase → _______ + 2Pi
cAMP
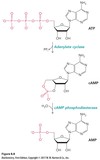
cAMP + cAMP phosphodiesterase → ___________
AMP (inactivated)

cAMP is a positive modulator that activates ________ _________ __ which activates many other kinases.
Protein kinase A
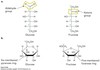
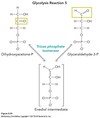
PIP2 + PLC → _____ + ______
DAG + IP3

Even though DAG and IP3 are both secondary messengers, how do they differ?
DAG - activates Protein kinase C (PKC) which phosphorylates target proteins - turns OFF glycogen synthesis
IP3 - opens Ca2+ channels on ER - turns ON glycogen degredation

How are signals amplified?

What is the structure of GPCR’s and what kind of perceptions are they involved in?
7 transmembrane α helices (serpentine) that are considered glycoproteins because carbohydrate functional groups are attached to the extracellular domain
N-terminus outside, C-terminus inside
Involved in sensory perceptions (vision, taste, smell)

What ligand binds to the ß2-adrenergic receptor?
Epinephrine
Compare agonists and antagonists.
Agonist - mimics natural ligand
Antagonist - binds to receptor but no structural changes occur (similar to inhibitors)

Primary receptors are mostly ___________.
hormones
Epinephrine has 2 pathways. What are they?
ß2-adrenergic receptor
α1-adrenergic receptor

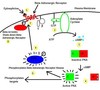
What is the general pathway for GPCR activation?
- Ligand binds to GPCR leading to a conformational change
- GTP replaces GDP in Gα subunit and subunits dissociate into Gα–GTP and Gβγ
- Downstream signaling
- Termination of signal

GPCR’s have __________ G proteins attached to them
heterotrimeric (3 different subunits)