Midterm - Voice Disorders Flashcards
(25 cards)
Muscle Tension Dysphonia
- caused by vocal hypertension - too much effort to phonate Primary - dysphonia Secondary - in presence of organic/phycogenic/neurologic problem, as compensatory strategy Treatment: head/neck relaxation, chant talk, chewing, digital manipulation, laryngeal massage, yawn-sigh
Ventricular Dysphonia
- interference of false vocal folds during phonation, usually a symptom of another problem - false folds shouldn’t approach midline
Psychogenic Dysphonia
- hoarseness that has no physical cause appears after emotional distress
Puberphonia
Voice doesn’t reflect development of secondary sex characteristics in puberty characteristics: pitch breaks, falsetto, strain treatment: masking, digital manipulations, glottal fry - hierarchy approach
Somatization Dysphonia
Shows symptoms beyond dysphonia (e.g., laryngeal pain, shortness of breath). Presents like a physical etiology, but there isn’t one. Features can include whisper voice or aphonia, very high or very low pitch, voluntary muteness. Treatment is centred around identification and reduction of the emotional and psychological factors.
Vocal Cord Nodules
- whitish growths on one or both of the vocal cords - callous-like growths
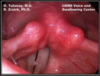
Vocal Cord Nodules

Vocal Cord Polyps
- one or both cords
- appear as fluid filled sacks
- larger than nodules
- blister like
- cord abuse over time or short term
Risks: hoarseness, breathiness or air wastage, decreased pitch range and loudness range, voice and body fatigue, Shooting pain from ear to ear
Treatments for Nodules & Polyps
medically, surgically, and/or behaviorally
Surgical intervention involves removing the nodule or polyp from the vocal cord. This approach only occurs when the nodules or polyps are very large or have existed for a long time.
This includes treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), allergies, etc. Medical intervention to stop smoking or to control stress is sometimes needed.
behavioral intervention/voice therapy from SLP/CDAs

Laryngitis
Hoarseness, Breathiness, Harsh voice, Strained voice, Low pitch
Treatment: rest, no whispering
Organic Voice Disorders
Related to structural deviations of the vocal tract, or to diseases of specific structures of the vocal tract
Laryngomalacia
Congenital Abnormality
- inward collapse of subglottic structures
- treatment - outgrown or surgery (5%)

Subglottal Stenosis
- narrowing of subglottal space
- congenital OR acquired (caused by repeated intubations at birth)
- treatment: close monitoring OR surgical intervention
Esophageal Atresia/Tracheoesophageal Fistula
- EA: esophagus ends in blind pouch
- TF: abnormal opening between eso and trac
- often occur together
- surgery immediately after birth followed by feeding therapy

Cancer
- carcinoma in vocal tract
- Tongue, palate, velum: Effects on articulation, vocal resonance, swallow.
- Larynx: Effects on voice, consequences for airway adequacy.
- treatment: surgery, radiation
Acid Reflux

Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is the passage of gastric juices from the stomach into the esophagus.
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease (LPRD) is the passage of contents superiorly into the pharynx
treatment: meds and diet

Granuloma
Granulated tissue that forms over contact ulcers on the arytenoid cartilages.
Causes:
Hard glottal attack, LPRD, intubation
Treatment: voice therapy; lower strain, jaw relaxation, lower volume (Confidential Voice), easy attack

Leukoplakia/Hyperkeratosis
Reactive epithelial tissue growth.
Thickened patches that are red (keratosis) or white (leukoplakia). Unilateral or bilateral. Causes: Smoking
Treatment: Monitor as a pre-malignant condition. Eliminate sources of irritation.

Papilloma
Wart-like growths, viral in origin (associated with certain strains of HPV).
Affects adults and children.
Treatment: Medical/surgical management to protect airway.

Laryngeal Webbing
Abnormal tissue forms between the VFs.
Can be congenital or acquired.
Signs and Symptoms: High-pitched cry/voice Stridor
Treatment: Surgical removal (sometimes grows back)
Neurogenic Voice Disorders
Related to damage or disease within the nervous system

Vocal cord paralysis (uni, bi)
- damage to CNX through head and neck injuries, tumors, disease, surgery, or stroke.
- Unilateral more common than bilateral.
- The paralyzed vocal cord does not move to vibrate with the other cord but vibrates abnormally or does not vibrate at all - surgery or injections
- head turn (toward paralysed side), digital manipulation, pitch shift
Spasmodic Dysphonia
Adductor type (more common)
- cords spasm closed during speech, sounds strained/strangled
Abductor type
- cords spasm open during speech, sounds breathy
- neurologic disorder
- cause unknown - trauma, viral infection, random


