Midtterm II Flashcards
(218 cards)

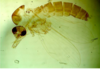
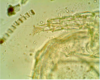
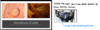
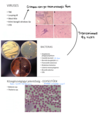
Goniodes dissimilis – a typical example of ischnoceran lice of birds. Members of this group are equally frequent on birds and mammals. Antennae are short but thin and never can be hidden into the head. An egg is in the abdomen
Chewing lice

Menopon gallinae - an example of amblyceran lice. Species of this group of lice are more frequent on birds than on mammals. Antennae are stout, short and can be retracted into cavities on both sides of head.
Chewing lice

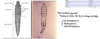
Columbicola columbae an ischnoceran louse of pigeons.
Chewing lice
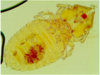
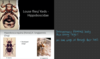
Felicola subrostratus: the only louse species of cat in Europe
Chewing lice

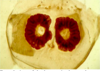
A nit of Felicola with lid is attached to hair. It contains egg yolk or embryo.
Chewing lice

A nit of Trichodectes without lid sits on hair with the first nymph inside before hatching.
Chewing lice

Adult Trichodectes canis grasps the hair with its mandibles. A claw on hind legs is seen. Only one claw on each leg is characteristic for each mammalian louse. (Avian lice have two.)
Chewing lice

Bovicola ovis nymph. Its first two legs embrace the hind part of the head. Only one claw on the tip of some legs can be seen. Particles of ingested hair are in the body as dark masses.
Chewing lice

An adult specimen of Werneckiella equi.
Chewing lice

A small nymph of Werneckiella equi.
Chewing lice

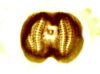
Haematopinus suis with equal sized legs and claws. Members of this genus are the biggest lice that live on livestock.
Blood sucking lice

Linognathus vituli First legs are smaller than the next ones, the head is elongated. On cattle.
Blood sucking lice

Solenopotes capillatus louse of cattle [For comparison only: NO DEMONSTRATION SPECIMEN] Similar to Linognathus but has a stouter head.
Blood sucking lice

S. capillatus has a wide head but it is slimmer than the distance between of the stems of first legs. [For comparison only! NOT SHOWN SPECIMEN!]
Blood sucking lice

Linognathus setosus louse of dog.
Blood sucking lice

A squashed nymph of Haematopinus from a nit.
Blood sucking lice

Male Pulex irritans. Male flea is smaller than the female. Chitinous copulatory organs as bent rods lay inside the abdominal part.
Fleas

Female Pulex irritans. A developing egg can be seen inside the abdomen as spherical mass. Dark masses are remnants of ingested blood.
Fleas

Ctenocephalides canis ♀
Fleas

Ctenocephalides canis ♂.
Fleas

Ctenocephalides canis.
Fleas

Ctenocephalides felis
Fleas

Tibia of the third leg of Ctenocephalides canis.
Fleas

Tibia of the third leg of Ctenocephalides felis.
Fleas