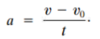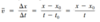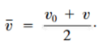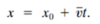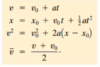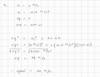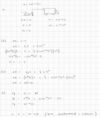Module 01: Kinematics Flashcards
Lesson 1.1 - Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration Lesson 1.2 - Motion at Constant Acceleration, Freely Falling Objects, and Graphical Analysis Lesson 1.3 - Vector Addition Lesson 1.4 - Projectile Motion (139 cards)
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
Define Mechanics:
Mechanics is the study of the motion of objects, and the related concepts of force and energy.
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What are the two fields of mechanics?
- Kinematics (description of how objectives move)
- Dynamics (deals with the forces and why objects move as they do)
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is translational motion?
Objects that move without rotating
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is the idealized particle?
- mathematical point with no spatial size (no size)
- Can only go through translational motion
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is a reference frame and why is it important?
Any measurement of position, distance, or speed needs a reference frame.
- Important to specify
- Need to say “with respect to Earth” to avoid confusion
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What are important aspects of the motion of an object?
(1) SPEED and (2) DIRECTION of motion
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
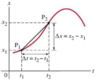
Define distance and displacement
Distance: Change in position of the object
Displacement: How far the object is from its starting point
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What are the components of a vector? Does displacement qualify?
Vectors have both (1) MAGNITUDE and (2) DIRECTION (and displacement qualifies)
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What does the sign of movement along a line (vector in one dimension)?
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is the formula for displacement?
Δx = x2 - x1
- Δx = Displacement
- x2 - x1 = Position Two minus Position One
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What does “speed” refer to?
How far an object travels in a given amount of time
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is average speed?
Total distance traveled along its path is divided by the time it takes to travel the distance

Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is the difference between velocity and speed?
- Speed: positive number (with units)
- Velocity: signify both (1) magnitude and (2) direction [meaning its a vector]
- Furthermore, the average velocity is displacement over time (rather than distance)
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is average velocity?
- Displacement divided by the elapsed time

Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
When does average speed and average velocity have the same magnitude?
If the motion of an object is along a straight line and in the same direction, the magnitude of displacement is equal to the total path length. In that case, the magnitude of the average velocity is equal to the average speed.
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
Define instantaneous velocity (and the formula).
- The average velocity over an infinitesimally short time interval*
- Evaluated in the limit of Δt becomes extremely small (approaching zero)
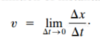
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
Why is the instantaneous speed always equal to the magnitude of the displacement?
because the distance traveled and the magnitude of the displacement becomes the same when they are infinitesimally small
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
When the average velocity and the velocity equal to each other?
When an object moves at a uniform velocity during a particular time
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is acceleration?
Specifies how rapidly the velocity of an object is changing
SI units of acceleration: m/s2
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is the average acceleration?
Velocity is divided by the time taken to make this change.

Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is instantaneous acceleration?
Analogy to instantaneous velocity as the average acceleration over an infinitesimally short time interval at a given time:

Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is deceleration?
- Object is slowing down
- Not mean that acceleration is necessarily negative
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What is the formula for displacement when the acceleration is constant?
Δx = vi Δt + 1/2 a (Δt)2
- Δx: displacement
- vi: initial velocity
- Δt: change in time
- a: acceleration (must be constant)
Lessson 1.1 - Speed and Velocity and Acceleration
What direction is acceleration when the velocity is negative?
Positive (acceleration is always the opposite direction than velocity)