MSK 4 - Lower Limbs Flashcards
(74 cards)
what is the popliteal fossa?
The popliteal fossa is a fat–filled diamond- shaped space located posterior to the knee joint. It is comparable to the ante-cubital fossa found in the upper limb
1

Biceps femoris: long head
2

Semimembranous
3

Semitendinosus
4

Tibial nerve
5

Popliteal artery
6

Common fibular nerve
What is the relation of the popliteal artery to the popliteal vein?
it lies medial and deep to it
Which muscles form the superior boundaries of popliteal fossa?
Medial – Semimembranous and semitendinosus
Lateral – Biceps femoris (long head)
Which muscle forms the inferior boundary of popliteal fossa?
Gastrocnemius
This important muscle is split and has a lateral and medial head, you will cover this in Part 2.
what is the contents of the popliteal fossa?
- Fat
- Common fibular nerve
- Tibial nerve
- Sural nerve
- Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- Popliteal Lymph Nodes and Vessels
(7. Termination of the lesser saphenous vein)
Remember that the popliteal artery is the continuation of the femoral artery as it emerges from the _______ ______\_
adductor hiatus

The posterior compartment of the leg is the _______ of the 3 compartments. The muscles in the posterior leg are divided into a superficial and a deep group
largest
Gastrocnemius powerful, two-headed muscle which dorsiflexes the ankle and is essential for a walking gait.
Which nerve innervates gastrocnemius?
Tibial nerve (S1, S2)
What is the function of the small muscle with its very long tendon, plantaris?
Plantar flex ankle joint and flex the knee joint, weakly assists in plantarflexion
a

Medial head of gastrocnemius
b

Lateral head of gastrocnemius
c

Aponeurosis of gastrocnemius
d
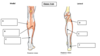
Soleus
e

Plantaris
f

Achilles Tendon
gastrocnemius
calcaneus
_ muscles make up the deep compartmen
4
1

popliteus































