MSK Flashcards
(11 cards)
Kanavel’s signs (4)
- Finger flexed at rest
- Symmetric enlargement, “sausage digit”
- Tenderness along course of flexor sheath
- Pain with passive extension
Tenosynovitis - Findings on US (3)
- Increased fluid content within tendon sheath
- Thickening of the synovial sheath with or without increased vascularity which can extend into the tendon sheath
- Peritendinous subcutaneous edema. This can result in a hypoechoic halo sign and peritendinous subcutaneous hyperemia on color doppler imaging

Tenosynovitis - How can US distinguish chronic from acute tenosynovitis
Color doppler US can differentiate between synovial thickening which is more indiative of chronic disease and
Turbid tendon sheath fluid collection - more indicative of acute exudative tenosynovitis
(In chronic inactive disease, however, there is synovial thickening with minimal vascularity)

De Quervain tenosynovitis - Presentation
Non-traumatic origin of pain on radial aspect of wrist. Painful thumb movements.
De Quervain tenosynovitis - US findings

Thickened sheath around the extensor pollicis brevis tendon

De Quervain tenosynovitis - US findings - Which two tendons involved, how to locate them
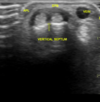
- Extensor pollicis longus = Most radial tendon when making the anatomical snuffbox
- Abductor pollicis longus = In common tendon sheath, more palmo-radial than EPL

Baker’s cyst - Location
Lies posterior to the medial femoral condyle

How is a baker cyst attached to the knee joint
Through a small valvular opening
(Knee effusion from intraarticular pathology (Most commonly osteoarthritis and meniscal tear) allows the fluid to go through the valve to the cyst in one direction)

Which two muscles is the Baker’s cyst located between
The semimembranosus and medial gastrocnemius muscles

Baker’s cyst - Presentation
Usually swelling behind the knee with pain, fullness and tenderness
(It is easier to see when the knee is fully flexed)
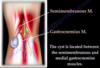
Baker’s cyst US aspiration - Position and technique
- The patient is in a supine position
- Start with transverse linear probe, will find baker cyst between semimembranosus and medial head og gastrocnemius (The upper and lower medial muscles)
- Scan longitudinally, check the extend proximal and distally
- Use color doppler to exlude vasculature
- In a longitudinal position, insert the needle from proximal and aspirate
- Scan the area after to ensure no evidence of bleeding in this area
(On picture tendon of semimembranosus marked in green, medial condyle of femur under, muscle of medial head of gastrocnemius (‘Starry night appearance’) down to the right, Baker’s cyst in the center (C-shaped))



