Neoplasia Flashcards
(97 cards)
This is endometrium. Which is hyperplastic? Is this pathological (what would cause it)

Right is hyperplasia –> physiologic hyperplasia
Due to increased hormones
What would cause the thyroid gland to look like this

Compensatory or pathologic hyperplasia (due to iodine deficiency)
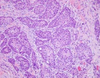
What cellular changes are going on here?

Metaplasia - shift from normal columnar to squamous epithelium (from basement membrane - not change in mature cells)
What’s a cause of bladder metaplasia

Vitamin A deficiency- change from transitional epithelium to squamous
What causes dysplasia
Persistent irritation or inflammation
What is abnormal pattern of tissue growth with atypical cells
Dysplasia
Why are dysplasic tissues significant
Pre-neoplastic change!
Label the cell changes. Which are cancerous?

5 and 6 are cancerous

What is loss of cellular differentiation called
Anaplasia
Is anaplasia reversible?
NO!
Are anaplastic cells considered benign, malignant, or both?
Malignant
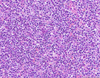
What type of cells are these arrows pointing to

Anaplastic cells (can see mitotic figures too)
Which cells are most, middle and least likely to undergo hyperplasia?
Most likely: epithelial cells (skin, hepatocytes, mucosa)
Medium likelihood: smooth muscle, bone, cartilage
Least likely: striated muscle
Is metaplasia neoplastic ? Is it reversible
Not neoplastic
It is reversible
You notice a growth to be pendunculated and encapsulated. It also appears to be expansile. Do these features suggest benign or malignant
Benign

A growth is infiltatrive. Would you consider this to be malignant
Yes - infiltrative neoplasms are usually malignant
What two growth behaviour features almost always indicate malignancy
Metastasis
Infiltrative
Fill in the chart


What are some gross features of a tumor that indicate malignancy
Necrosis
Hemorrhage
Both indicate its outgrown its blood supply
Is this likely benign or malignant
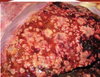
Malignant
- Necrosis
- Hemorrhage
- Infiltrative (lack of distinct borders)
Biliary carcinoma
Is this likely benign or malignant
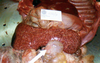
Malignant
- Infiltrative (spleen is enlarged)
- Lymphoma*
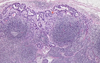
Is this likely benign or malignant

Malignant
- Invasive
- Hemangiosarcoma*
Which is benign? Which is malignant?

Left: benign
- Distinct borders (not infiltrative)
- Pedunculated
Right: malignant
- Infiltrative
- No demarcation from surrounding tissue
- Necrotic

Benign or malignant?

Malignant
- No demarcation
- Infiltrative
Oral fibrosarcoma