Neuro WEEK 12 PT 1 (1-7) Flashcards
(157 cards)
Striatum
Caudate nucleus & the Putamen
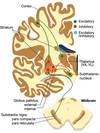
Substantia Nigra is comprised of
cell rich Pars compacta & fiber rich Pars reticulate
Basal Nuclei Includes
Caudate nucleus, Putamen, Globus Pallidus, Substantia Nigra & Subthalamus
Basal Nuclei also includes the: PeNS
Pedunculopontine nucleus Nucleus Accumbens Subthalamic nucleus
Where is the Pedunculopontine nucleus located?
in brainstem just caudal to substantia nigra.
The Pedunculopontine N is part of the
Ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending connections thru reticulospinal tracts to LMNs
Nucleus Accumbens is also known as
ventral striatum
Which system is the Nucleus Accumbens densely connected with?
limbic system.
Nucleus Accumbens is a part of which pathway? MMR
mesolimbic motivation & reward pathway
What runs through specific parts of the basal nuclei?
Distinct, parallel operating circuits or loops
Naturally occurring disorders of the basal ganglia such as Parkinson’s disease (PD) or Huntington’s disease (HD) may affect
multiple loops
Symptoms presented with basal ganglia disorders such as Parkinson’s disease (PD) or Huntington’s disease (HD) - MEC
- Motor
- Emotional
- Cognitive,
What is the key to basal nuclei function in motor activities?
Disinhibition.
Thalamocortical (VA/VL to motor cortex) projections are
Excitatory (glutaminergic)
In order for the thalamus to excite the cortex, basal nuclei must
Physically remove the inhibition of the motor nuclei of the thalamus (VA/VL).
Excitatory (glutaminergic) motor nuclei are tonically inhibited (GABAnergic) by
Globus pallidus & substantia nigra pars reticulate
Removal of inhibition of disinhibition is done by
The striatum via the GPi in the direct pathway
Indirect pathway begins with excitatory glutaminergic pathway from
Cortex to striatum.
In the indirect pathway striatal GABAnergic inhibitory neurons produces inhibition of inhibitory GABA output from
GPe to subthalamus.
In the indirect pathway, the disinhibited subthalamus excites
GPi (again with glutamate).
What happens when the GPi is excited in the indirect pathway? .
The VA/VL thalamus is inhibited & cortex can no longer be excited - motor cortex will not produce movement
what type of movement does the indirect pathway inhibit?
voluntary movement
Balance of the direct & indirect pathways produces
movement or not.
Pars Reticulata is very similar in structure and function to
Globus pallidus internus.


