Neuroanatomy Flashcards
(45 cards)
Neuraxis
Imaginary line drawn throught the spinal cord to the front of the brain.

Rostral - Caudal
Anterior - Posterior
Rostral: toward the nose
Anterior: toward the front
Caudal: toward the tail
Posterior: toward the rear

Ventral - dorsal
Inferior - superior
Ventral: toward the front
Inferior: below
Dorsal: toward the back
Superior: above

Medial - Lateral
Medial: toward the midline
Lateral: away from the midline
NB: midline is the medial line of the body which divides the body into halves that are mirrror images of each other

Nervous system

Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
Voluntary control/senses
Autonomic Nervous System
Subsconscious body control: visceral function, heart rate, respiration rate, digestion, salivation, pupil dilation, sexual arousal
- Efferent nerves
- Parasympathetic nervous system
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Afferent nerves
Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
Rest and digest
- Eyes: accommodation for near vision (miosis)
- Saliva: copious liquid
- Heart: rate and blood pressure down
Sympathetic nervous system
4 Fs:
- Fight
- Flight
- Fright
-
Fuck
- Eyes: pupillary dilation
- Saliva: little, viscous
- Heart: rate, force and blood pressure up
- CNS: drive and alertness up
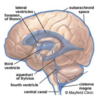
Hindbrain (metencephalon and myelencephalon)
Brain stem (midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata) and cerebellum

Cerebellum
Involved in motor control especially voluntary movement, body position and motor learning.
Contains 50% of total neurons in brain
Grey and white matter
Known as ‘little brain’
Pons
Bridge between cerebrum and cerebellum + medulla oblongata
Siutated on top of the brainstem
Brainstem
Midbrain + pons + medulla oblongata
Connects spinal cord with forebrain and cerebellum

Formatio reticularis (reticular formation)
Regulates activity/sleep

Medulla oblongata
Relays motor and sensory signals between the spinal cord and higher brain regions.
Reflex control centre (ANS) e.g. heart rate

Midbrain
Tectum (dorsal) + tegmentum (ventral) + periaqueductal gray (PAG)

Tectum
- Inferior colliculi
- Auditory function
- Superior colliculi
- Visual function
Inferior colliculi
Auditory functino
Superior colliculi
Visual functio
Tegmentum
Substantia nigra + red nucleus
–> Voluntary movement control
Periaqueductal gray (PAG)
Tissue around the cerebral aqueduct that connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles

Forebrain (telencephalon and diencephalon)
- Diencephalon
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
- Telecephalon
- Cortex
- Basal ganglia
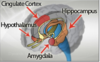
- Limbic system