Neuropathology Flashcards
(83 cards)

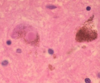
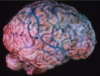
Ischemic damage - Purkinje cells

Laminar necrosis

Laminar necrosis
Ischemic cell death of cortex

Hypoxic encephalopathy

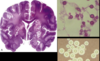
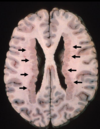
Multiple Sclerosis
Periventricular plaques

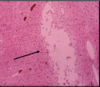
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
Opportunistic JC virus
Invasion and destruction of oligodendrocytes

JC virus inclusions in oligodendrocytes

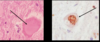
Necrotizing vasculitis

Normal –> axonal degradation in peripheral nerve

Onion bulb formation in Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoeuropathy

Diabetic neuropathy
Axonal degradation and reduplication of capillary basement membrane

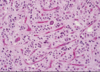
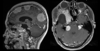
Infarcts in watershed zone

Arteriolosclerosis

Lacunar infarct due to arteriolosclerosis
Occlusion of small penetrating arteries

Lacunar infarct due to areteriolosclerosis

Hemorrhagic infarct secondary to cardiac embolism

Hypertensive hemorrhage
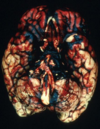
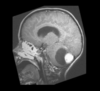
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Caused by Berry aneurysm
What is this. What are the complications of this?

Berry aneurysm
Rebleeding
Vasospasm
Fibrosis of subarachnoid space

Arteriovenous malformation

Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Name/grade of tumor
Name of protein that stains positive
MRI enhancing: Y/N?
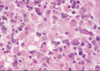
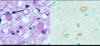
Low grade astrocytoma
GFAP positive
Non enhancing

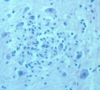
Anaplastic astrocytoma
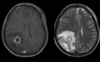
Name, characteristics, ring enhancing?

Glioblastoma multiforme
Pseudopallisading necrosis and microvascular proliferation
Ring enhancing - due to breakdown of BBB