NREMT Flashcards
(40 cards)
The pathway of blood through the heart
superior/inferior vena cava right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle lungs for oxygenation pulmonary valve left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle aortic valve aorta.
Beck’s Triad consists of what 3 signs?
Muffled heart tones, hypotension and jugular vein distension
What blood pressure is represented when the ventricles are filling with blood?
Diastolic
triad of symptoms that indicates abdominal aortic aneurysm
abdominal pain, hypotension, and pulsating abdominal mass
There are two types of valves in the heart. The mitral and tricuspid valves are which kind of valve?
Atrioventricular
Semilunar valves of the heart include…
The pulmonic and aortic valves are both semilunar valves.
What is the preferred method of ventilation in the field for a patient who is not able to breathe on his own?
Mouth-to-mask ventilation
Types of bronchodilators include all of the following EXCEPT: Alupent Pulmicort Proventil Metaprel
Pulmicort
The three signs of imminent respiratory failure in a patient experiencing acute respiratory distress:
The three signs of imminent respiratory failure in a patient experiencing acute respiratory distress: - cyanosis - decreased consciousness - inability to maintain respiratory effort
List the presentation of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
ARDS: - hypotension - diaphoresis - tachynpea - dyspnea - dizziness/confusion - exhaustion - cyanosis - edema - absent lung sounds
Steps of assessment
Pulse airway is open and clear respiratory rate and depth & work of breathing level of oxygenation level of consciousness
Ataxic respirations
completely irregular breathing punctured by periods of apnea (cessation of breath)
Cheyenne-Stokes respiration
characteristic form of ataxic respiration—a pattern in which breathing deepens progressively and occasionally becomes progressively more rapid as well, punctured by periods of apnea. Pattern repeats in a cycle taking from 30s-2 minutes
What is the normal rate of breathing for someone who is 6-12 months old
24-30 breaths/minute
What is the normal rate of breathing for someone who is 1-6 years old
1-6 yo = 20-30 breaths/min
What is end tidal CO₂? How is it measured and what does an elevated value and a decreased value represent?
End tidal CO₂ is the amount of CO₂ present in exhaled gases and is measured by capnography. Elevated end tidal CO₂ = hypoventilation or increased metabolic activity Low end tidal CO₂ = decreased cardiac output, low pulmonary perfusion
Recovery position is recommended for patients who are (conscious/unconscious) and (breathing spontaneously / not breathing spontaneously)
Recovery position = unconscious + NOT breathing spontaneously

Bone 2 = fibular
Bone 3 = tibia (think tibia = taler = wider & fatter than fibular)
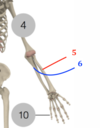
Bone 4 = Humerous
Bone 5 = Radius (lateral)
Bone 6 = Ulnar (medial)
Bone 10 = Phalanx
Three layers of the skin?
- Epidermis
- Dermis
- Subcutaneous

- Mandible
- maxilla
- nasal bone
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- zygomatic bone
- sphenoid bone
RUQ main organ (2)
organs present here and also in other areas (4)
RUQ = Liver + gallbladder
also right kidney, colon, pancrease, small intestines
LUQ main organ (2)
organs present here and also in other areas (4)
LUQ = spleen + stomach
Other = liver (small portion), left kideny, colon, pancreas, small intestines
RLQ main organ (1)
organs present here and also in other areas (3)
RLQ: Appendix
Other: utererus, colon, right ovary


