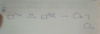ochem final Flashcards
(79 cards)
in an E1 elimination
- the base removes a proton from the beta carbon in the first step
- the base removes an atom from the beta carbon in the second step
- the leaving group departs from the alpha carbon in the first step
- the leaving group departs from the alpha carbon in the first step
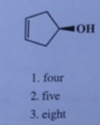
the stereo chemistry of the highligted carbon in the following compound is
1 r
2 s
3 neither

R

which of the following reactions exhibits primary kinetic isotope effect>
- Sn2
- E1
- E2
3 E2

which reactions are entropically favored
- eliminations
- substitutions
- additions
1 Eliminations

(2S,3S) -2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid ( the alpha amino acid L isolucine) has a specific rotation of 41* the stereoisomer (2r,3R) -2-amino-3- methylpentanoica acid has a specific rotation that
- is -41.0*
- is 0*
- cannot be predicted
1 -41*

which compound is the most reactive toward nuclephilic substitution
1 1,2- epoxypropane
- 1-methoxypropane
- propan-1-ol
3 propanol
alchohols can act as
- acid only
- base only
- either acid or bases
3 either acid or bases
Sn1 reactions afford
- complete retention of configuration
- racemization or partial inversion of configuration
- complete inversion of the configuration
2 racemization or partial inversion of configuration
phenols are more acidic than alchohols due to
- sterics
- resonance stabilization of the corresponding conjugate base
- increased nucleophilicity
2 resonance stabilization of the corresponding conjugate base
which carbo cation is the least stable?

1

which of the following compounds has the most exothemic heat of hydrogenation
- hex-1-ene
- trans hex-3-ene
3 (Z)-3-methylhex-3-ene
hex-1-ene

2 which of the following compounds is least likely to have its molecular ion appear in its electron impact mass spectrum ?

1

if a compound has a molecular formula of C8 H14 which of the following functional groups are possibly present
- cyclic diene
- acyclic alkyne
- benzing ring
2 acyclic alkyne

Simmons Smith cyclopropanation of 1,2disubstituted alkenes is
- non-diastereoselective
- partially diastereoselective
- completely diastereoselective
2 completely diastereoselective
which nucleus has a higher equilibrium population excess of its alpha spin state
1 1H
- 13C
- both have the same population excess
13C
Sn2 reactions occur with
- no sterochemical control
- partial stereochemical control
- complete stereochemical control
3 complete stereo chemical control
Sn2 reactions always occurs with complete stereochemistry control, because every time the nucleophile attacks, it always do for the opposite side of the leaving group.
PCC oxidation of a primary alchohol affords the corresponding
- carbocylic acid
- aldehyde
- ester
- PCC is a great nucleophile to oxydize alcohols. Depending of the type of alcohol, it can be oxydize to ketones or aldehydes. 2nd and 3rd alcohols gets oxydized to ketones, and 1st alcohols are oxydized to aldehydes.
Oxidation of 1-butanethiol with dilute hydrogen peroxide yields
- 1 an alcohol
- sulfide
- disulfide
. You will get from here an alcohol.
epoxides are reactive compounds due to
angel strain
torsional strain
steric strain
Angel strain
which of the following compounds is an aromatic

Compound b) is aromatic basically because it’s double bonds are conjugate, and the rule 4n+2 it’s done:
4n + 2 = 10 electrons –> n = 2
which reaction often yields product mixtures due to rearrangements
Sn1
Sn2
E2
Sn1
other factors being equal a more electronegative leaving group makes an Sn2 reaction proceed
slower ‘
faster’
same rate
Slower
the stereochemical configuration ofthe following diol is

S
the following reaction is

partially enantioselective and completely diastereoselective