Off Pump CABG & Mechanical Circulatory Devices - Quiz 7 Flashcards
(50 cards)
What are the different approaches for doing a CABG?
Thoracotomy - minimally invasive
&
Full Sternotomy
Other than the Surgeon & Anesthetist, who else is also required to be in the room for a CABG?
Perfusionist w/ a CPB machine ready
An Off-Pump CABG usually takes _____ time than a traditional CPB CABG
An Off-Pump CABG usually takes MORE time than a traditional CPB CABG
What makes a pt. a good candidate for an Off-Pump CABG?
Good LV Function
How does Fluid Management differ from an On-Pump CABG vs an Off-Pump CABG?
Harder to give large amt of fluid Off-Pump unlike the CPB Machine that can give large amounts extremely quickly
Normothermia is absolutely necessary during a CABG. What are ways to maintain normothermia?
Monitor Core Temp
Water Thermoregulation Mattress
Heat Preserving Bouffant
↑Room Temp
What can happen if a pt does not maintain normothermia of 36o C during a CABG?
Will be unable to Extubate
Which Antifibrinolytic is normally given for an On-Pump CABG, but NOT given for an Off-Pump CABG?
Aminocaproic Acid (Amicar) - inhibits Plasminogen binding to Fibrin converting it to Plasmin
What is the dose of Heparin given for an Off-Pump CABG?
Less than it would be for On-Pump CABG
100-200 units/kg w/ a goal ACT > 300
(sometimes full heparin @ 300-400 units/kg)
What is the reversal for Heparin?
Protamine
How is the heart visualized during an Off-Pump CABG?
Surgeon uses Footplate Stabilizers & Retractors that Suction & Lift the Heart
How is the Blood Pressure managed during Verticalization of the Apex to visualize the PDA & Circumflex?
Keep MAP Elevated & Give Volume to counter Extreme Hemodynamic Compromise & Ischemia
At what point during an Off-Pump CABG does the MAP need to be lowered to 60 mmHg?
During the Proximal Graft Aortic Anastomosis
What are the Advantages of an Off-Pump CABG?
Less Bleeding
Less Heparin
Normothermia Maintained –> Potential Extubation
No Aortic Cross-Clamp
Why are Intra-Aortic Ballloon Pumps (IABP) used?
↑Cardiac Perfusion w/ Sync’d Counterpulsation
↑Coronary Blood Flow on Diastole
↓Afterload on Systole
Stabilizes PreOP CABG Pts post MI
What is used as a supplement for an Off-Pump CABG or for patients who have difficulty coming off the CPB machine?
Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP)
What are contraindications for placing a pt on a IABP?
Sepsis
Descending Aortic Disease
Severe PVD
Severe Aortic Regurg.
What site is the IABP inserted?
Via Femoral Artery
For an Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump, where does the Tip of the Balloon lie?
At the Junction of Aortic Arch & Descending Aorta
&
2 cm distal to the origin of Left Subclavian Artery
How does the Timing of an IABP work?
Timed w/ Dicrotic Notch & Inflates on Diastole when AV Closes to seal and increase pressure, sending blood to the coronary arteries
When does the IABP deflate?
Deflates right before Systole at the beginning of the R-Wave
What does IABP Deflation do?
Vacuum Effect
↓Aortic Pressure & ↓Afterload
Facilitates Ventricular Ejection
↓O2 Demand
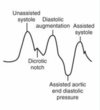
What is happening here?

Premature Deflation during Diastole
Suboptimal Perfusion
Backflow
Angina
↑O2 Demand
What is happening here?
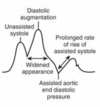
Deflation in Late Diastole as AV Begins to Open
No Afterload Change or ↑Afterload
↑O2 Demand
Prolonged Isovolumetric Contraction