Operative Dentistry Flashcards
(148 cards)
What is the chemical formula for Hydroxyapatite?
Ca10(PO4)(OH)2

_______ is the main component of enamel and dentin.
carbonate-substitute hydroxyapatite (CHA)

Discuss the shape of an enamel rod or prism in regards to what is the weakest part:
Enamel rods have a head and a tail. The tail tends to be more organic and have less mineral content thus making it more susceptible to decay.
***BOARDS***

How does carbonate-substituted hydroxyapatite affect the solubility of enamel?
Carbonate-substitution increases solubility of hydroxyapatite (easier to decay)
On the outer part of enamel has more fluoroapatitite making it more difficult to decay. The closer you go to the DEJ in enamel the more carbonate-substitution their is making it easier to decay.
The deeper the cavity prep the more soluble (easier to decay) the hydroxyapatite . So closer to the DEJ the easier the tooth will decay

Discuss how bacteria demineralizes teeth:

Discuss the Stephan Curve in regards to each of the following:
- What is the pH of the mouth normally?
- What is the critical pH of tooth enamel? (The pH where tooth will begin demineralizing)
***ALWAYS ON BOARDS (Stephen Curve)***
Mouth = pH 7
Critical pt = pH 5.5

What are the 3 benefits of fluoride?
- Remineralization of tooth structure (shifting equilibrium to the left)
- Decreasing enamel solubility (lowering the critical pH)
- Interfering w/ metabolic activity of cariogenic bacteria
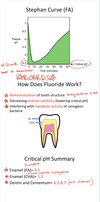
What is the critical pH for each of the following:
- Enamel (FA- Fluoroapatite) = ?
- Enamel (CHA- carbon-substituted hydroxyapatite) = ?
- Dentin and Cementum = ?
Critical pH
Enamel (FA) = 4.5 pH (harder to demineralize)
Enamel (CHA) = 5.5 pH
Dentin and Cementum = 6.2-6.7 pH (more vulnerable)

Discuss Caries in regards to each of the following:
- What is the ADA definition of caries?
- Modified Keyes-Jordan diagram?

Discuss the progress of lesions in regards to each of the following:
- Pit and fissure lesions shape = ?
- Smooth-surface lesions shape (interproximal) = ?
- Root-surface lesions shape = ?
***FORSURE BOARDS Q***

Deeper, dry, leathery, demineralized but not invaded by bacteria describes which of the following:
A. Infected dentin
B. Affected dentin
B. Affected dentin

Superficial, wet, soft mushy and necrotic are all characteristics of which of the following?
A. Infected dentin
B. Affected dentin
A. Infected dentin

Discuss the progression of lesions in regards to each of the following:
- Intact surface?
- Cavitation?
- How long may it take to form an actual enamel cavitation (cavity)?

What is the correct order of the progression of a carious lesion?
- Dentin cavitation
- Enamel cavitation
- Enamel demineralization
- Dentin demineralization
***HE GOT A BOARD Q ON THIS***
Enamel demineralization –> Dentin demineralization –> Enamel cavitation —> Dentin cavitation

Which of the following is on smooth surface, appears opaque white when air-dried and seems to disappear when wet?
A. Incipient/Reversible lesion
B. Cavitation/Irreversible lesion
A. Incipient/Reversible lesion

________ is characterized as enamel surface is broken (not intact) and usually the lesion has advanced into the dentin.
A. Incipient/Reversible lesion
B. Cavitation/Irreversible lesion
B. Cavitation/Irreversible lesion

Which of the following is characterized as: covers three or more surfaces of a tooth (MOD, MODFL)?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
C. Complex caries
Simple = one surface
Compound = 2 surfaces
Complex = 3 or more surfaces

Which of the following is characterized as: covers one surface of a tooth (Occlusal)?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
A. Simple caries
Simple = one surface
Compound = 2 surfaces
Complex = 3 or more surfaces

Which of the following is characterized as: covers two surfaces of a tooth (MO, DO)?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
B. Compound caries
Simple = one surface
Compound = 2 surfaces
Complex = 3 or more surfaces

Which of the following is characterized as: occurs at junction of tooth and restoration indicating microleakage?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
D. Secondary caries
- Secondary caries = junction of tooth and restoration
- Residual caries = caries that remain in a completed tooth prep

Which of the following is characterized as: caries that remain in a completed tooth prep?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
E. Residual caries
- Secondary caries = junction of tooth and restoration
- Residual caries = caries that remain in a completed tooth prep

Brown/black, hard, caries-resistant if exposed to fluoride (dentinal lesion has sclerotic dentin) describes which of the following?
A. Acute/Rampant caries
B. Chronic/Slow caries
C. Arrested caries
D. Primary caries
C. Arrested caries

Rapidly damages tooth structure, light-colored, soft, infectious describes which of the following?
A. Acute/Rampant caries
B. Chronic/Slow caries
C. Arrested caries
D. Primary caries
A. Acute/Rampant caries

Demineralized tooth structure that is almost remineralized, discolored and fairly hard describes which of the following?
A. Acute/Rampant caries
B. Chronic/Slow caries
C. Arrested caries
D. Primary caries
B. Chronic/Slow caries