Operative Positioning Flashcards
What is the purpose of operative positioning? (list 3)
- comfort
- patient safety
- surgical exposure and or surgical access
Who is responsible for supervising and assuring no nerve or soft tissue injury and minimize physiological changes?
the anesthetist
How should you establish position changes?
gradually, particularly at the conclusion of long surgeries
The most imporant thing an anethetist can do while positon a patient is:
be vigilant!
What needs to be documented in regards to patient positioning?
- baseline ROM
- Intraoperative position
- use of padding
- body position
- checks done and frequency
What is the OR table weight limit?
136kg (200 lbs)
How long is the OR table?
80.7 inches
Is this proper hand position for a supine patient in the OR?

Yes, but be careful that the stuff behind the arm supporting it is not too rigid, otherwise you could damge the radial nerve.
How should the feet be,while in the supine position?
- not hanging off the bed
- heels padded
How do you supply lumbar support while in the supine position in the OR?
- slight flexion of hips and knees
- Pillow under the knees (caution)
- Legs/ feet should not be crossed
- TEDs/ SCDs increase venous return, decrease risk of DVT
- Safety strap
If you put too many pillows under the knees what would happen?
You could obstruct venous blood flow
What are the 5 mechanisms of nerve injury?
- stretching
- compression
- kinking
- ischemia
- transsection
The brachial plexus goes through what 2 fixed points.
- the verterbral foramina fascia
- axilla
What 3 things in the OR for the patient in supine positon, would cause injury to the brachial plexus?
- neck extension or head turned to one side
- when arm board extended or abducted >90 degrees
- arm/ arm board falls of the table (mostly stretching injuries)
What are the symptoms of a brachial plexus injury?
- electric shocks or burning sensation shooting down the arm
- numbness or weak arm
- no or weak motor control of shoulder and elbow
- pain
How does radial nerve damage occur in the OR?
compression of the radial nerve on the lateral aspect of the humerus from surgical retractors, ether screen, mismatched arm board, repeat BP inflation
What is the physiological result of radial nerve injury in the OR?
- wrist drop
- weakness in abduction of the thumb
- numbness 1, 2 ring fingers
What is the most common peripheral nerve injury obtained in the OR?
Ulnar nerve injury
What 2 types of injuries can occur to the ulnar nerve in the OR?
- It is in the cubital tunnel at the elbow groove. Compression of the nerve between the olecranon of the ulna and medial epicondyle of the humerus (entrapment with arm extension)
- Also injured by stretch with severe elbow flexion, dislocation with pronation of the hand, nerve dislocation over medial epicondyle w/stretching, compressing against bed
What 4 things happen with claw hand, what nerve is injured?
Claw hand is an ulnar nerve injury.
- Inability to abduct or oppose the 5th finger
- Weak grip ulnar side of fist
- Loss of sensation to the palmar surface to the 4th or 5th fingers
- Atrophy of intrinsic muscle of the hand (side of the hand)
What can you do to reduce injury to the ulnar nerve? (list 5)
- pad the arm boards
- avoid downward compression by strap
- assure surgical personnell don’t compress the patient’s arm
- Place BP cuff proximally so it doesn’t compress the ulnar groove or cubital tunnel
- Avoid prolonged flexion of the elbow
How common is the occurence of lower extremity nerve damage from the lithotomy position?
1 in 3608 patients
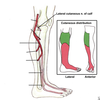
What percentage of lower extremity nerve injuries are to the common peroneal nerve?
78%
What percentage of nerve injuries are to the sciatic nerve?
15%