Ophtalmology Flashcards
(30 cards)
What’s your diagnosis?
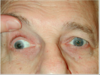
Oculomotor palsy
A lesion at #2 would give you which type of vision?

Complete monoocular visual loss of right eye (OD)

What’s your diagnosis?

Abducens nerve palsy: unopposed medical rectus because of disabled lateral rectus
What can cause horizontal diplopia?
LR (CN VI) or MR (CN III) problem
A lesion at #4 would give you which type of vision?

Left homonymous hemianopsia

RighA lesion at #3 (Meyer’s loop) would give you which type of vision?
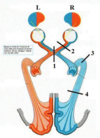
Left superior quadrantanopsia

What nerve is responsible for corneal reflex?
- CN V
- CN VII
A lesion at #1 would give you which type of vision?

Bitemporal hemianopsia

What are the 2 important questions to assess diplopia?
- What does the patient mean?
- If it is two images, is the problem monocular or binocular?
What is the function of cones?
Colors with low sensitivity to light (no colour vision with poor illumination)
What is the function of rods?
Colors for low illumination vision only
What nerve is responsible for pupillary reflex?
CN III
What can cause Horner’s syndrome?
- Lateral brainstem or cervical spinal cord lesion
- Superior cervical ganglion (“Pancoast” lung tumor)
- Carotid artery dissection
Dilation of the pupil is under the control of which system?
Sympathetic
What happens if you have a narrow angle of anterior?
Accumulation of aqueous humour that leads to acute glaucoma
Constriction of the pupil is under the control of which system?
Parasympathetic
What’s your diagnosis?

Trochlear nerve palsy: unopposed inferior oblique due to desabled superior oblique
Normal visual field but decreased visual acuity is a sign of lesion where?
Ocular (Cornea, Lens, vitreous)
Decrease visual acuity if a sign of lesion where?
- Ocular (Cornea, Lens, vitreous)
- Retina/Optic Nerve
What is the problem if the diplopia is binocular?
Diplopia is caused by misalignment of the two eyes
What can cause vertical diplopia?
IR (up, CN III) or SO (down, CN IV)
What is the fovea?
The point of maximum concentration of photoreceptors (mostly cones)
- Miosis
- (Mild) Ptosis
- Reduced Sweating
What’s your diagnosis?
Horner’s syndrome
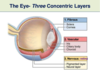
What are the layers of the eye?