Ophthamology Flashcards
(200 cards)
Amblyopia
Lazy eye
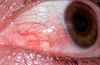
Types of chronic conjunctivitis
Vernal keratoconjunctivitis
Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
Features of vernal keratoconjunctivitis
- Children
- Seasonal
- FH of atopy
- Bilateral
- Ulceration and infiltration of upper cornea
Features of atopic keratoconjunctivitis
- Adults
- Associated with atopy
- Bilateral
- Can cause corneal ulceration and scarring
Neonatal conjunctivitis
Ophthalmia neonatorum
Usually secondary to N. gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis
Causes of acute red eye
Lids:
- Blepharitis
- Chalazion
- Malposition
Conjunctiva:
- Conjunctivitis
Sclera:
- Episcleritis
- Scleritis
Cornea:
- Keratitis
Uveal tract:
- Uveitis
Trabecular meshwork:
- Acute glaucoma
Periorbital skin:
- Preseptal cellulitis
- Orbital cellulitis
Presentation of Acanthamoeba keratitis
Pain
Red eye
Dendritiform epithelial lesions
Non-suppurative ring
Fungal keratitis presentation
Red eye
Photophobia
Blurred vision
Discharge
Anisocoria
Difference in pupil size > 4mm
Management of fungal keratitis
Topical antifungal
Corneal graft if unresponsive
Topical anti-fungals
Natamycin
Amphotericin

Hyphaema - blood in anterior chamber
Hypopion
Pus in anterior chamber
Orbital cellulitis presentation
Decreased vision
Unwell pt
Unilateral swollen eyelids
Ophthalmoplegia (reduced eye movements)
Proptosis
Orbital cellulitis Mx
Ophthalmological emergency
CT scan
IV antibiotics
Scleritis presentation
Extremely painful - often wakes at night
Cellular infiltration or entire sclera thickness
Red eye
Scleritis complications
Ischaemia and necrosis
Scleral thinning (Scleromalacia perforans)
Globe perforation
Scleritis prognosis
Can be self limiting
Central (/Branch) Retinal Artery Occlusion definition
Commonly embolisation from carotid artery
Central (/Branch) Retinal Artery Occlusion presentation
Painless
Possible RAPD
Retinal pallor
Cherry red spot
RAPD
Relative afferent pupillary defect
Paradoxical dilatation of directly stimulated pupil
Cherry red spot
At macula
Retina thinner - see underlying choroid
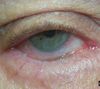
Entropion
Entropion definition
Inward turning of lid margin
Malposition of eye lid